Treating the Pain in Your Shins
Shin splints, or medial tibial stress syndrome, are among the most common overuse injuries in runners, athletes, and active individuals. The hallmark is pain running down the inner edge of your shinbone (tibia), which runs along the front of your lower leg. Pain along the front of your lower leg is a hallmark of shin splints.
Shin splints involve inflammation of the muscles, tendons and bone tissue in the front of your lower leg. Activities such as running, jumping, or high-intensity training often trigger the problem. What starts as a dull ache can quickly turn into stubborn discomfort that derails training, affects daily mobility and even increases the risk of more serious injury.
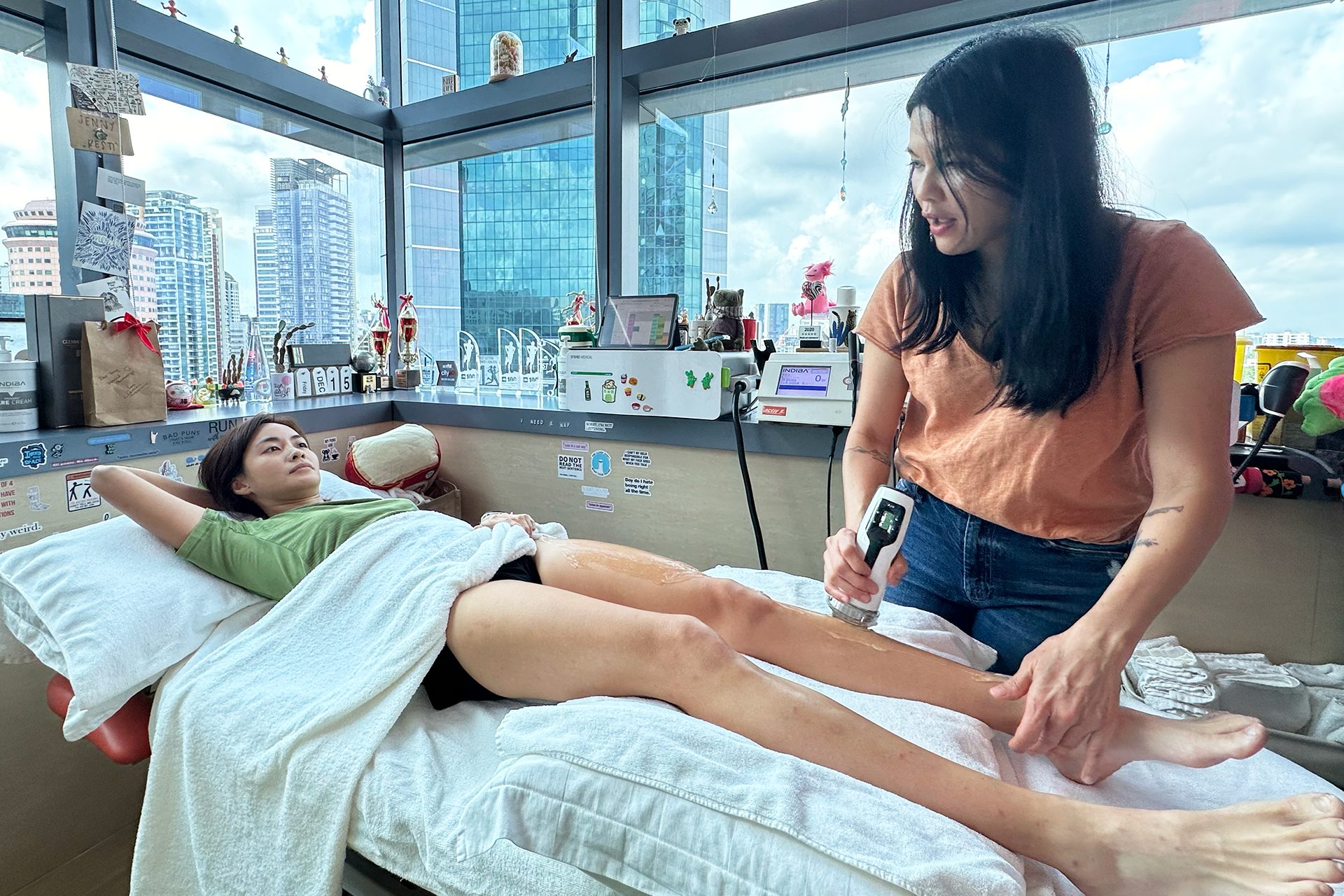
At HelloPhysio, we approach shin splints holistically. Shin splints rarely stem from a single cause; effective treatment must address overuse, mechanical overload, and biomechanical imbalances simultaneously. Overuse leads to stress on the muscles, tendons and bones of the lower leg, resulting in pain along the tibia. Our approach combines manual physical therapy with advanced modalities, such as INDIBA® and Shockwave Therapy, supported by targeted exercise programs to accelerate healing, restore function, and reduce the risk of recurrence.
What Are Shin Splints?
Shin splints occur when repetitive stress irritates the tibia and the soft tissues attached to it, causing inflammation and microtears. A shin splint is a specific overuse injury of the lower leg. Runners, dancers and military recruits are typical sufferers, though anyone who ramps up their activity too quickly can be affected.
The pain usually creeps along the inner shin, flares with exercise, and eases with rest. Symptoms of shin splints include diffuse aching, tenderness, mild swelling and pain that worsens with activity. Unlike fractures, which cause sharp, pinpointed pain, shin splints feel like a diffuse aching discomfort over a broader area of the bone. Recognising this difference is key to accurate diagnosis and timely treatment.
Why Shin Splints Happen
Shin splints are often the result of training errors, biomechanical quirks and lifestyle factors combining in the wrong way. Pushing mileage or intensity too fast, or running on hard, unforgiving surfaces, can overload the tibia. A person’s activity history, including recent changes in training or intensity, is important in understanding the risk for shin splints.
Biomechanics matter too. Flat feet, high arches, or overpronation alter the way forces are distributed through your legs, causing your shinbone and surrounding muscles to bear more stress than they can handle. Weak or tight calf muscles, limited ankle mobility, and poor hip strength can all contribute to the issue. Even footwear plays a role. Shoes with worn-out soles or inadequate arch support fail to absorb shock properly, passing the impact straight into your shins. Over time, these stresses accumulate, leading to persistent inflammation and pain that can worsen without intervention.

Shin Splints Symptoms
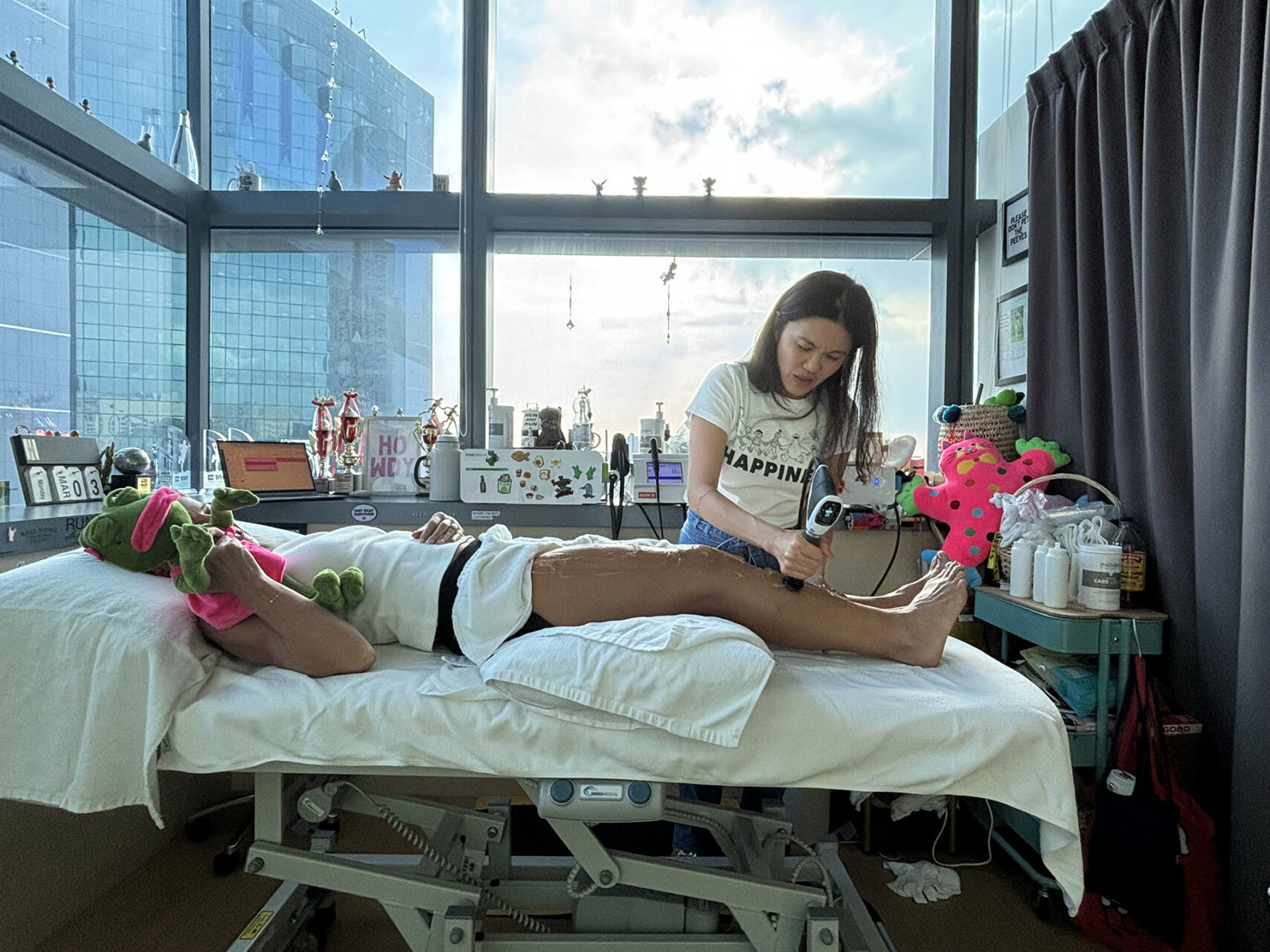
The most common symptom of shin splints is a dull ache along the inside of the shinbone. Initially, it may only appear at the beginning of the exercise and gradually ease off as you warm up. If ignored, it can persist throughout training and linger long after, becoming sharper with prolonged or intense activity.
You may also notice tenderness when you press along the tibia, mild swelling or stiffness in the lower leg. In more severe cases, the discomfort can radiate outward, and even walking can be uncomfortable. Recognising and addressing these symptoms early is key to avoiding stress fractures or long-term shin pain.

How Shin Splints Are Diagnosed
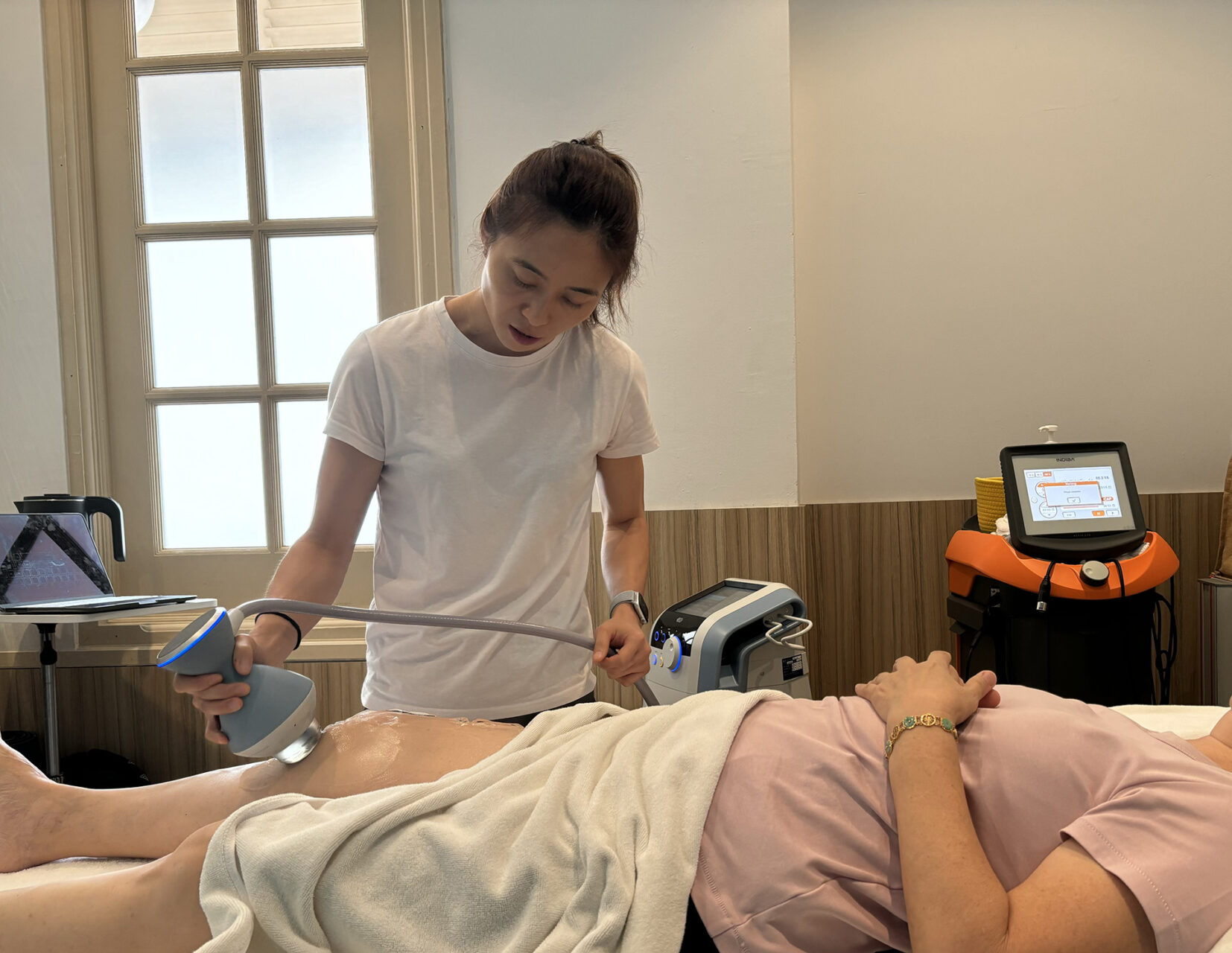
A physiotherapist begins with a thorough assessment, asking about your training habits, footwear and exact symptoms. They then examine your shin for tenderness, swelling, and movement patterns, including a physical exam of the front of your lower leg for tenderness, swelling, and movement patterns.
Imaging is not always necessary, but it may be used to rule out other conditions. X-rays can spot stress fractures, and MRIs or ultrasounds can provide detailed views of the soft tissues.

Complications and Risks of Shin Splints
While shin splints are common for runners, dancers and anyone increasing their activity levels, ignoring the pain can lead to more serious complications. One of the most significant risks associated with shin splints is the development of a stress fracture, a small crack in the shin bone caused by ongoing stress on the bone tissue. A stress fracture can cause sharp, persistent pain and may require you to stop all weight-bearing activities, sometimes needing crutches or a walking boot for proper healing.
Suppose you have shin splints and continue to push through the pain. In that case, you may also experience chronic inflammation or even long-term leg pain that interferes with daily activities and exercise routines. In some cases, untreated shin splints can contribute to other conditions such as tendonitis or compartment syndrome, which may require more intensive treatment.
If your symptoms are not improving or the pain is severe, you should see your doctor. They may recommend an X-ray or other imaging to rule out a stress fracture or other causes of shin pain. Early intervention is crucial in preventing the pain of shin splints from developing into a more serious injury.
Physiotherapy Treatments for Shin Splints
Conservative management is the first and most effective approach to treating shin splints, and physiotherapy plays a central role in this approach. At HelloPhysio, we design shin splint treatment plans that alleviate immediate pain while addressing the underlying causes.
Initial Care: The first step is to reduce irritation. Rest from high-impact activities, icing and modifying exercise routines all help to ease acute symptoms. To manage shin splints, consider the following steps: stretch your calf muscles, strengthen your lower leg muscles, gradually increase your activity levels, and consult a healthcare professional if the pain persists. Supportive shoes or orthotics may be introduced to correct alignment and reduce strain. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help to control inflammation while you begin rehabilitation.
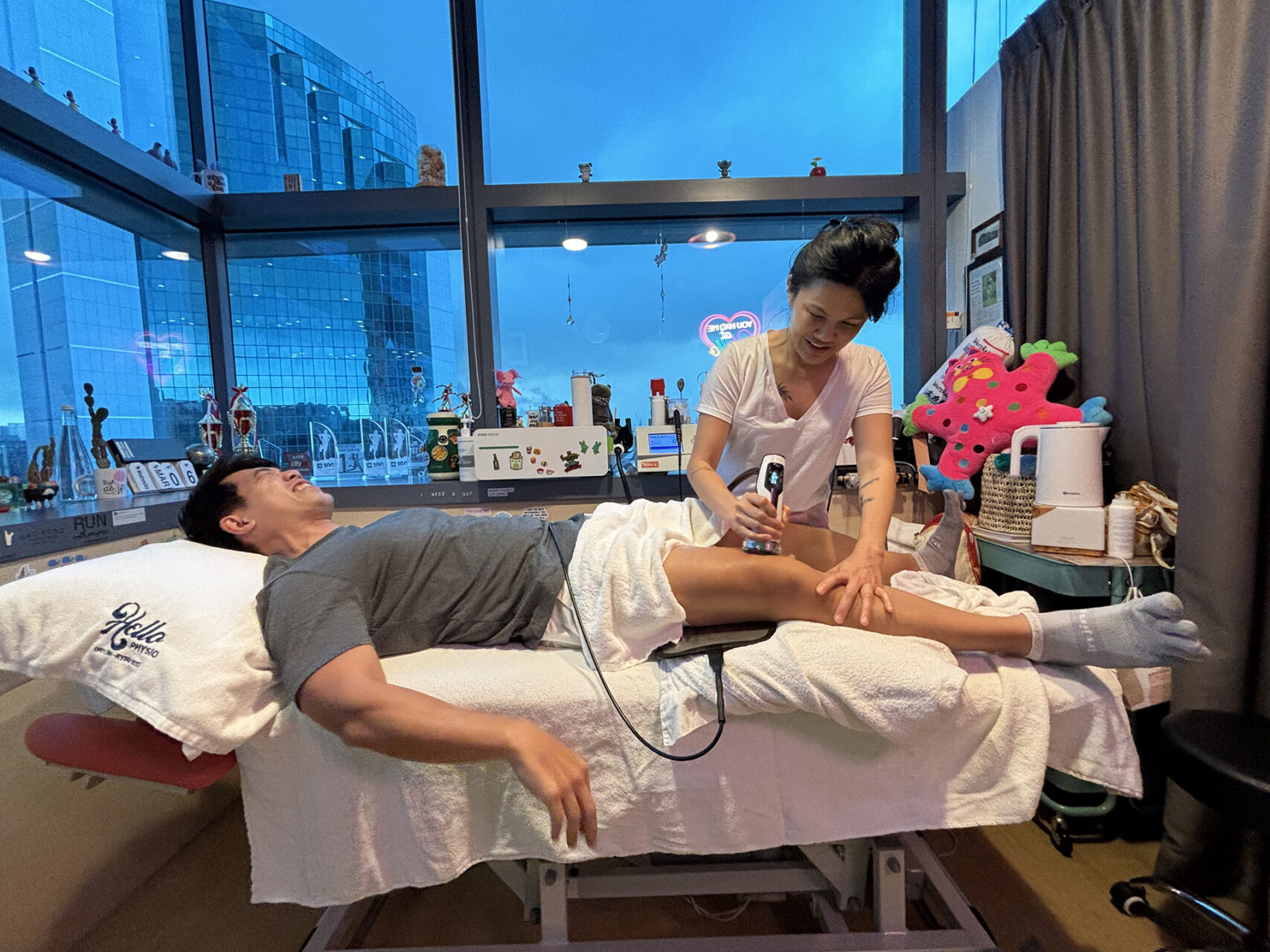
Advanced Therapies: As healing progresses, adjunct therapies are used to accelerate recovery. INDIBA utilises radiofrequency energy to stimulate cellular repair, enhance blood flow, and reduce inflammation, thereby helping tissues repair more quickly and with less discomfort. Shockwave Therapy directs acoustic waves into the injured tissues, stimulating blood vessel formation, breaking down scar tissue, and encouraging fresh cell growth, especially effective for stubborn or chronic shin splints.
Exercise Rehabilitation: Movement is medicine when prescribed correctly. Physiotherapists use progressive structured exercises to rebuild strength, flexibility and stability in the lower legs. Calf stretches, eccentric-loading drills, and balance training retrain muscles to handle stress more efficiently. Beyond the shins, hip and core strengthening, gait retraining, and Clinical Pilates help restore proper movement patterns across the entire lower body. High-impact activities are initially scaled back, with lower-impact options introduced to maintain fitness. As symptoms improve, activity is gradually increased to ensure your legs adapt safely without aggravating the condition.

Shin Splints Recovery Time
Shin splints recovery time varies depending on severity, activity level and how closely treatment plans are followed. Mild shin splints typically resolve within 2 to 4 weeks. More severe cases can take 6 to 12 weeks. Patience and adherence are key. Returning to complete training too quickly often leads to reinjury.
Prevention
Preventing shin splints involves balancing training load with proper body mechanics. Gradually increasing mileage, wearing supportive shoes, stretching the calf muscles and strengthening the lower legs are key. Cross-training with lower-impact activities, such as swimming or cycling, helps reduce repetitive stress. Working with a physiotherapist to identify and address biomechanical issues can make all the difference in preventing shin splints from recurring.
The HelloPhysio Approach
At HelloPhysio, we believe no two cases of shin splints are the same. That is why we begin with a detailed assessment of your gait, biomechanics, strength and lifestyle. Shin splints physio treatment blends manual therapy, INDIBA® Activ, Shockwave Therapy and tailored exercise rehabilitation to address both pain relief and long-term prevention. By treating the whole picture rather than just the symptoms, we aim to help you heal stronger and avoid reinjury. Book with HelloPhysio today.

