|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Hamstring strain injuries are among the most common injuries affecting athletes and active individuals. These injuries range from mild overstretching to significant tears, resulting in pain, reduced mobility and a prolonged recovery process. Understanding the causes of hamstring strain, how to prevent hamstring strain, and the role of physiotherapy in recovery is essential for effective treatment and long-term prevention.
Hamstring Strain Causes
A hamstring strain occurs when the muscles at the back of the thigh are overstretched or torn, often due to rapid acceleration, sudden deceleration, or overstretching of the leg. Insufficient warm-up or muscle preparation before intense activity is a common cause, leaving the muscles vulnerable. Muscle imbalances between the quadriceps and hamstrings, poor flexibility and fatigue further increase the risk of strain. The severity of the injury is classified into three grades:
- Grade 1 (Mild): Slight overstretching or minor tearing of muscle fibers, causing tightness and discomfort, and a minimal loss of function. Recovery typically takes 1-3 weeks with appropriate physiotherapy and rest. First-degree hamstring strain recovery time can be shortened with advanced treatments like INDIBA® Activ.
- Grade 2 (Moderate): Partial tearing of the muscle, leading to noticeable pain, swelling and difficulty moving. Recovery may take 4-8 weeks, depending on the extent of the damage.
- Grade 3 (Severe): Complete muscle tear, resulting in significant pain, bruising and inability to bear weight. Severe injuries may require three months or more and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Common symptoms include sudden pain, tenderness and difficulty walking or running. Proximal hamstring strain (near the glutes) and upper hamstring strain are particularly challenging due to their impact on hip mobility and strength.
Hamstring Cramp vs. Strain
It is important to differentiate between a hamstring cramp and a strain. A cramp is a sudden, involuntary muscle contraction that resolves quickly, while a strain involves damage to the muscle fibers. Persistent symptoms like swelling, bruising and restricted movement are indicative of a strain and require medical attention and rehabilitation.
Can You Run with a Hamstring Strain?
Running with a hamstring strain, especially a Grade 2 or 3 injury, is not advisable as it can exacerbate the damage. However, with a Grade 1 hamstring strain, light jogging may be possible if guided by a physiotherapist to ensure safety and proper healing. A common question, “Can I run with a Grade 1 hamstring strain?” is best answered with caution and professional guidance to avoid setbacks.
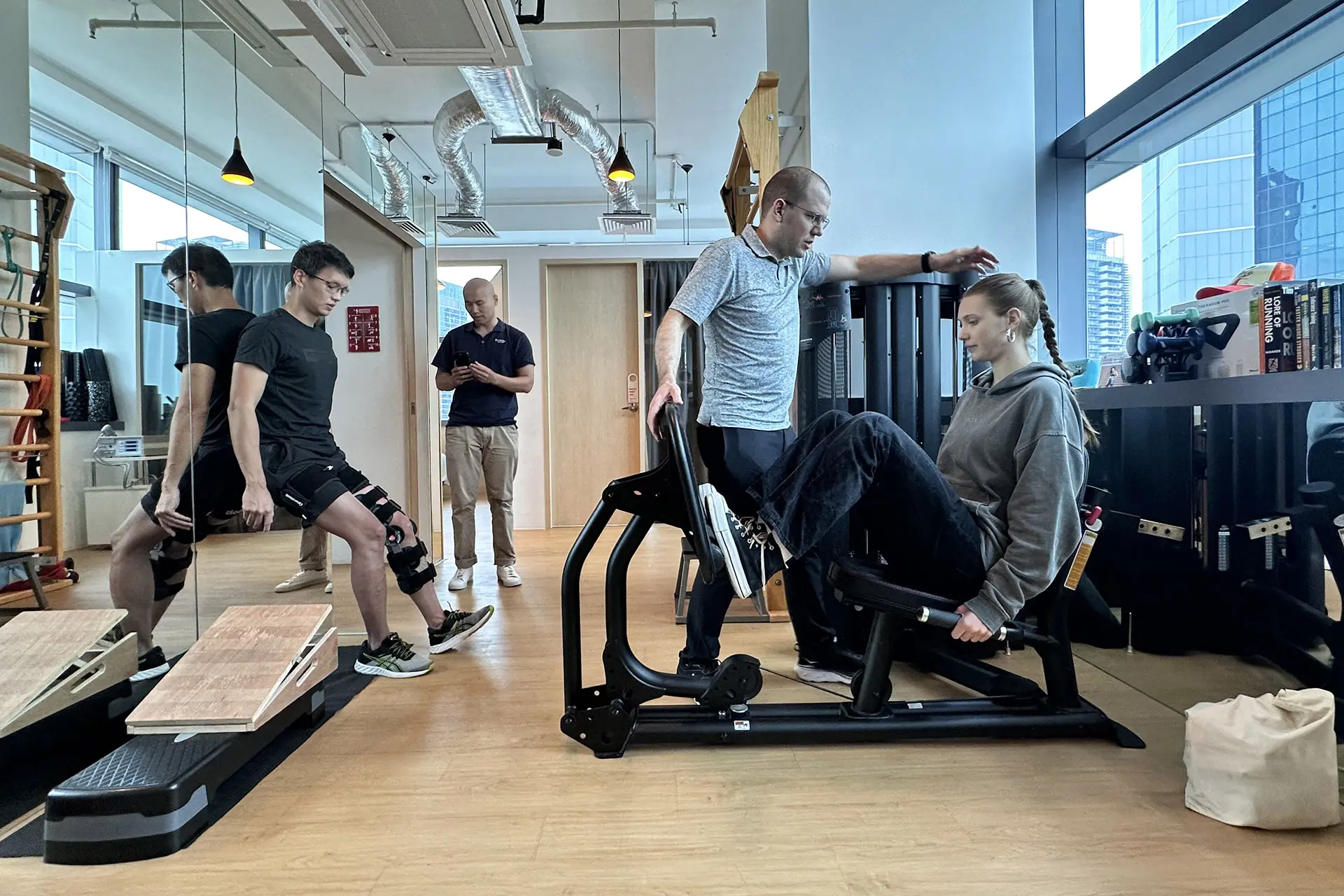
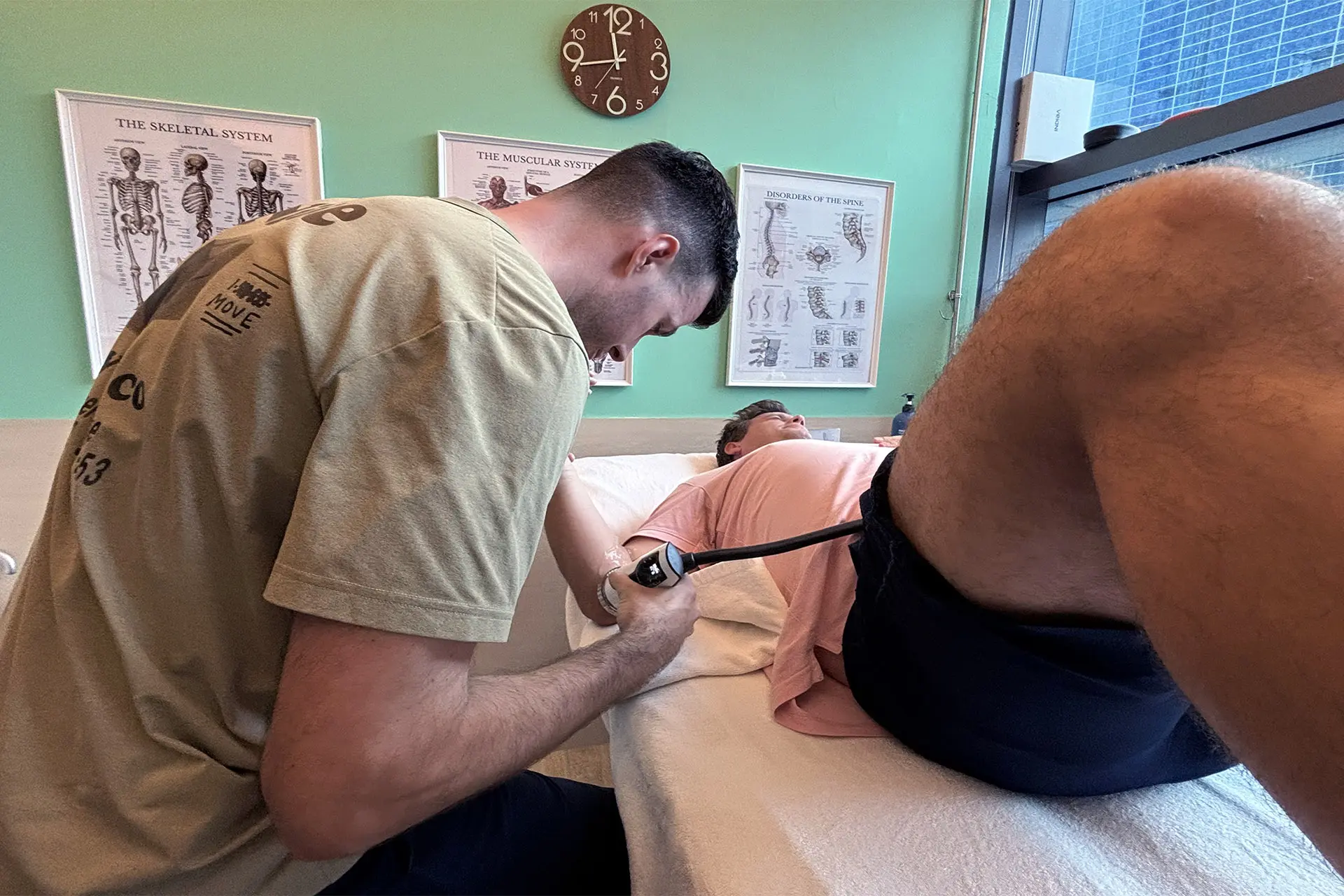
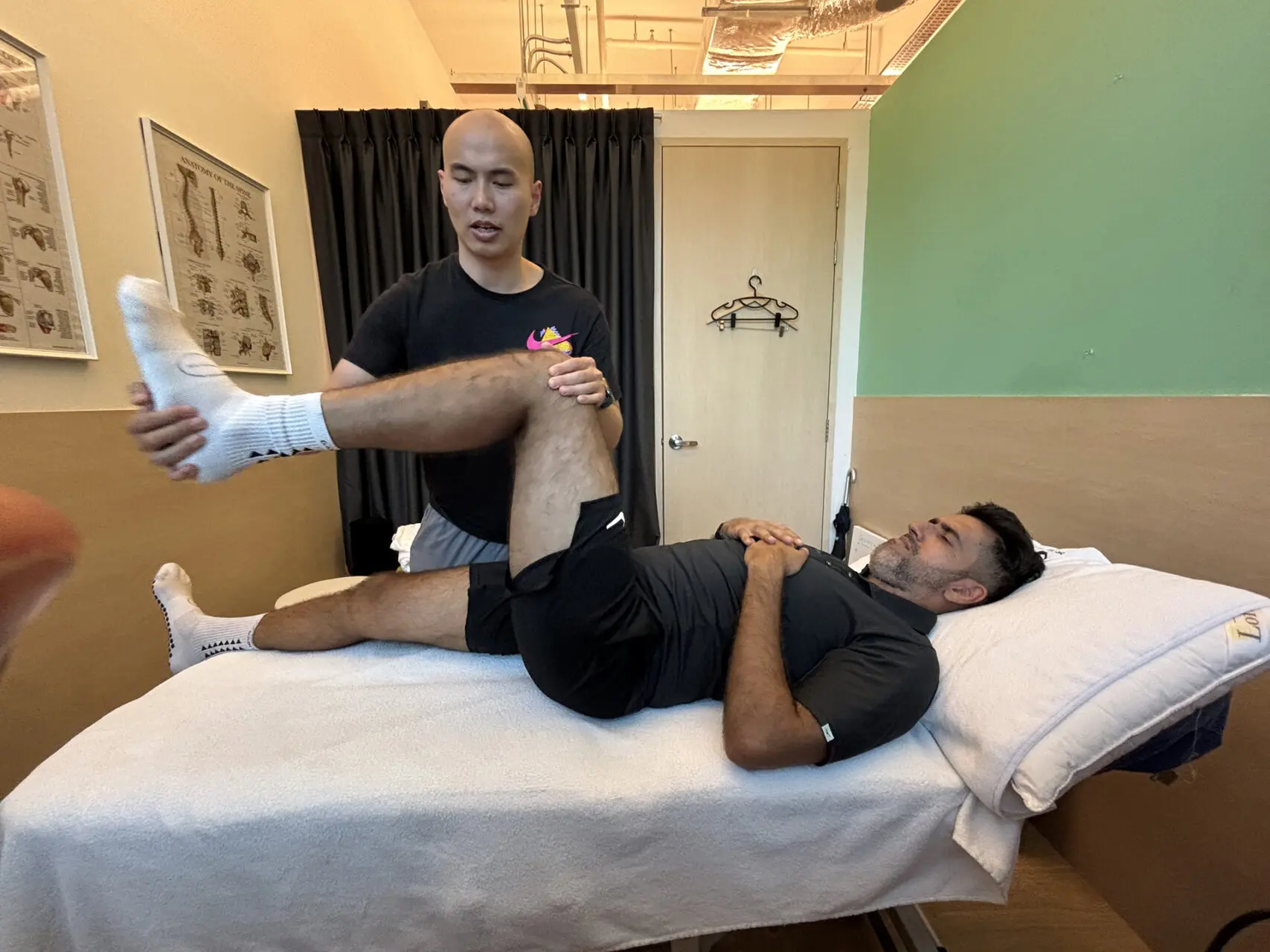
Hamstring Strain Diagnosis and Rehabilitation
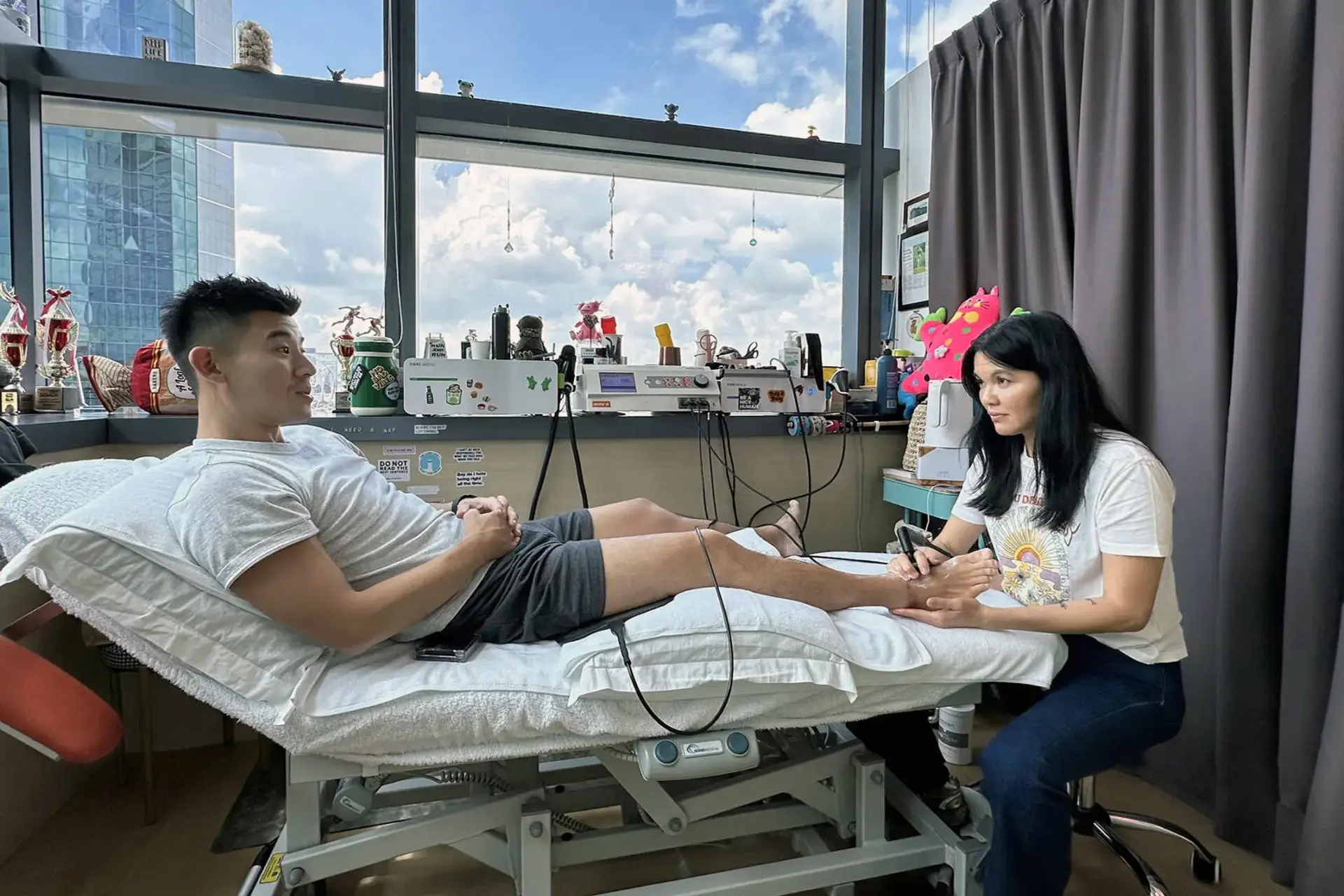
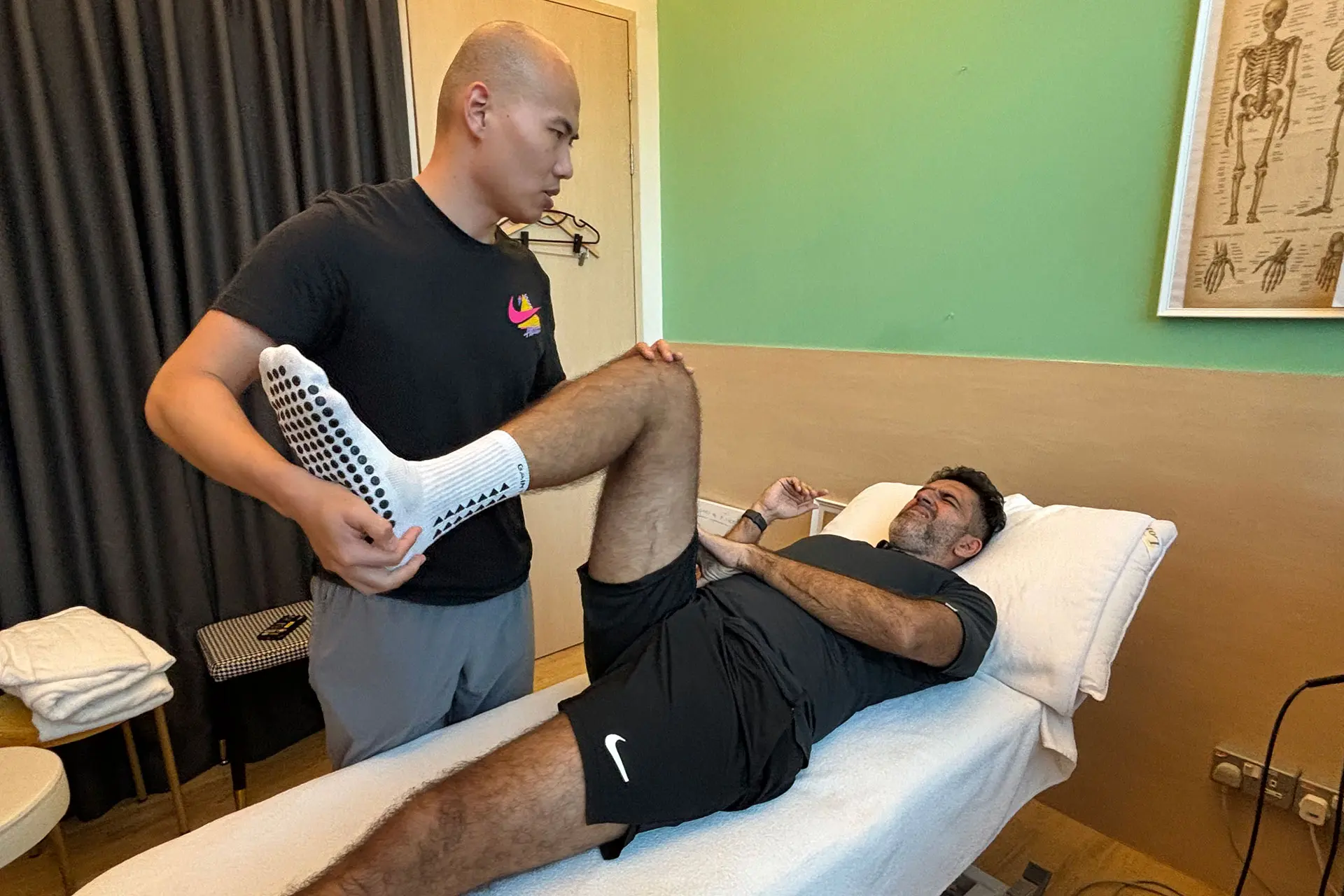
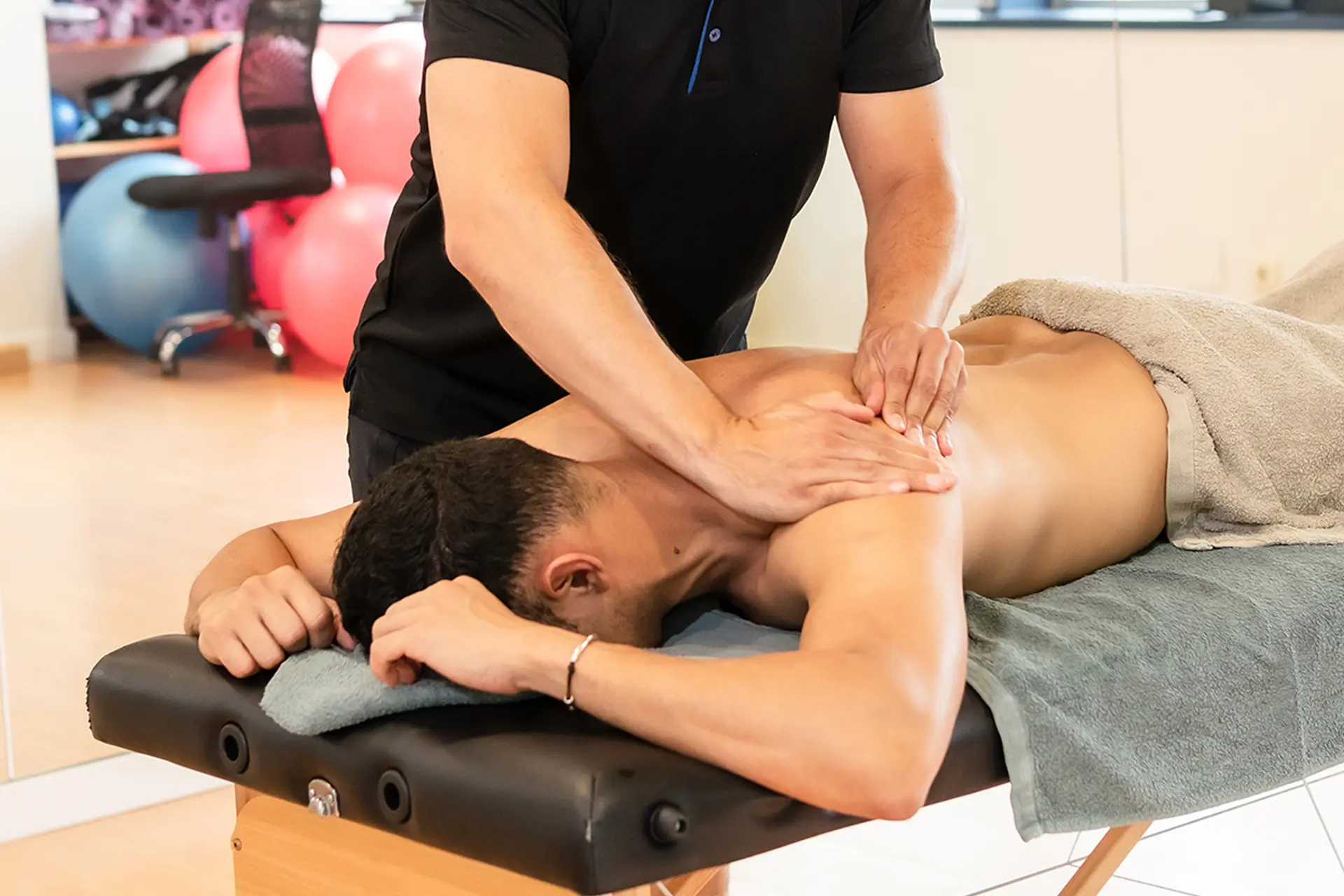
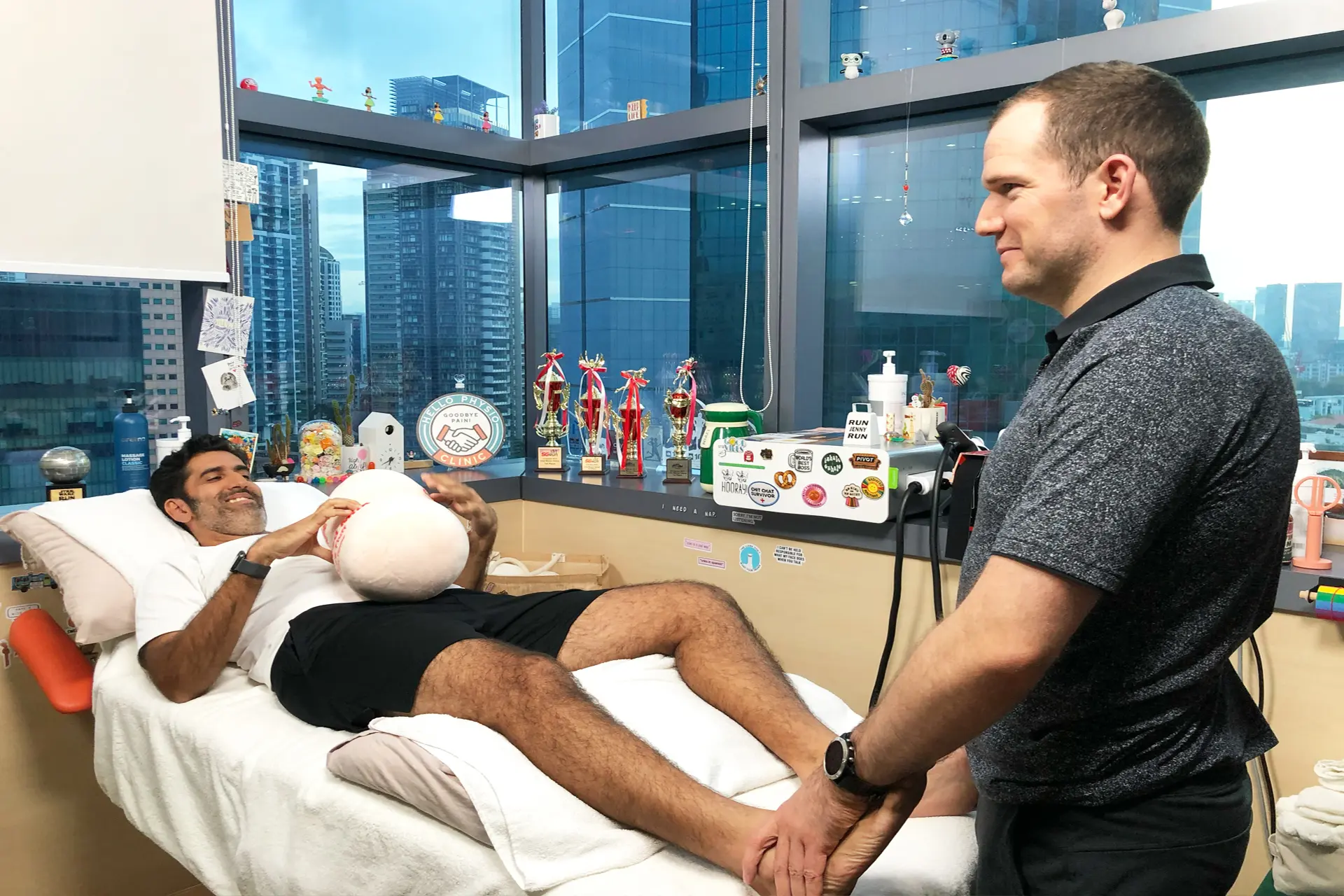
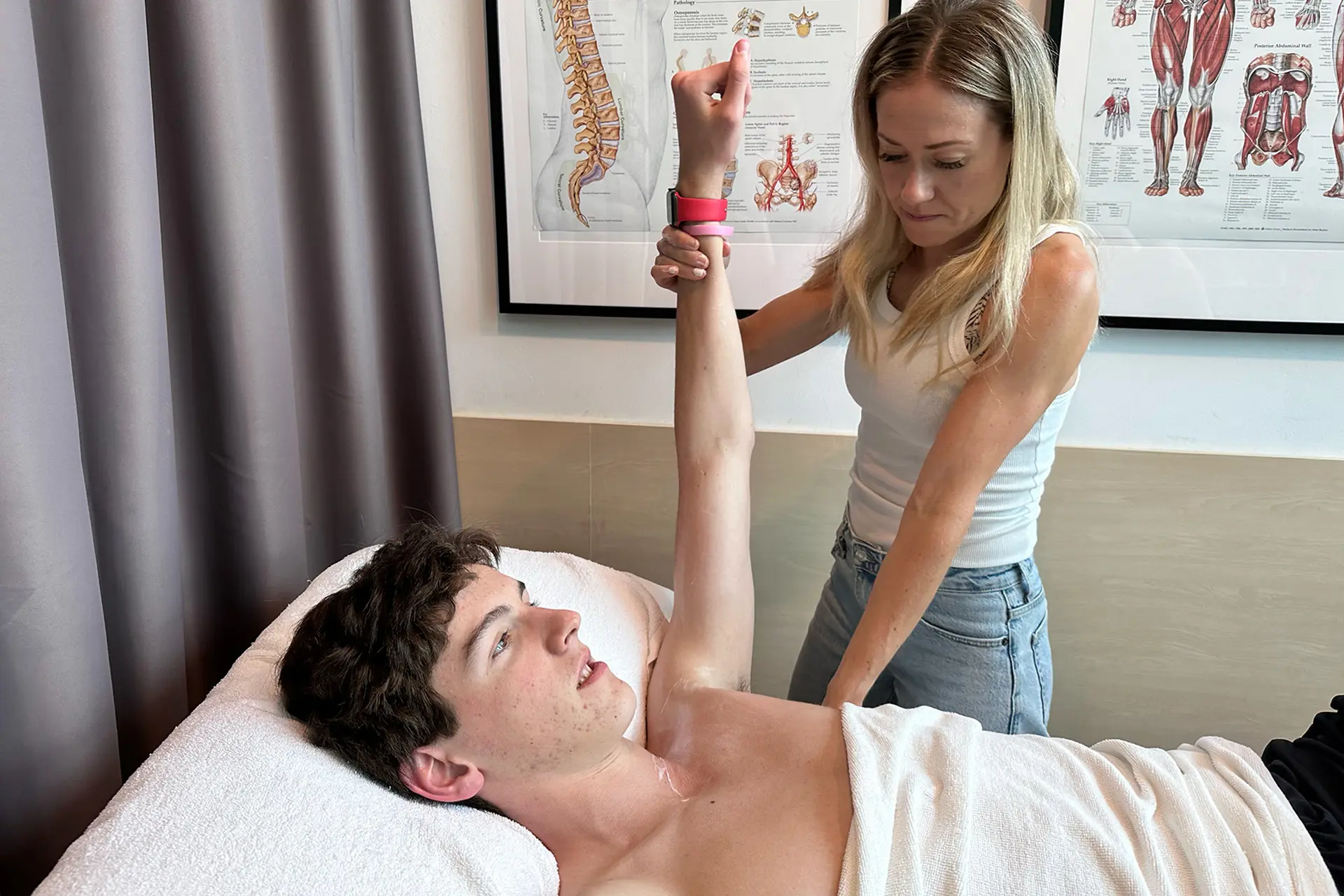
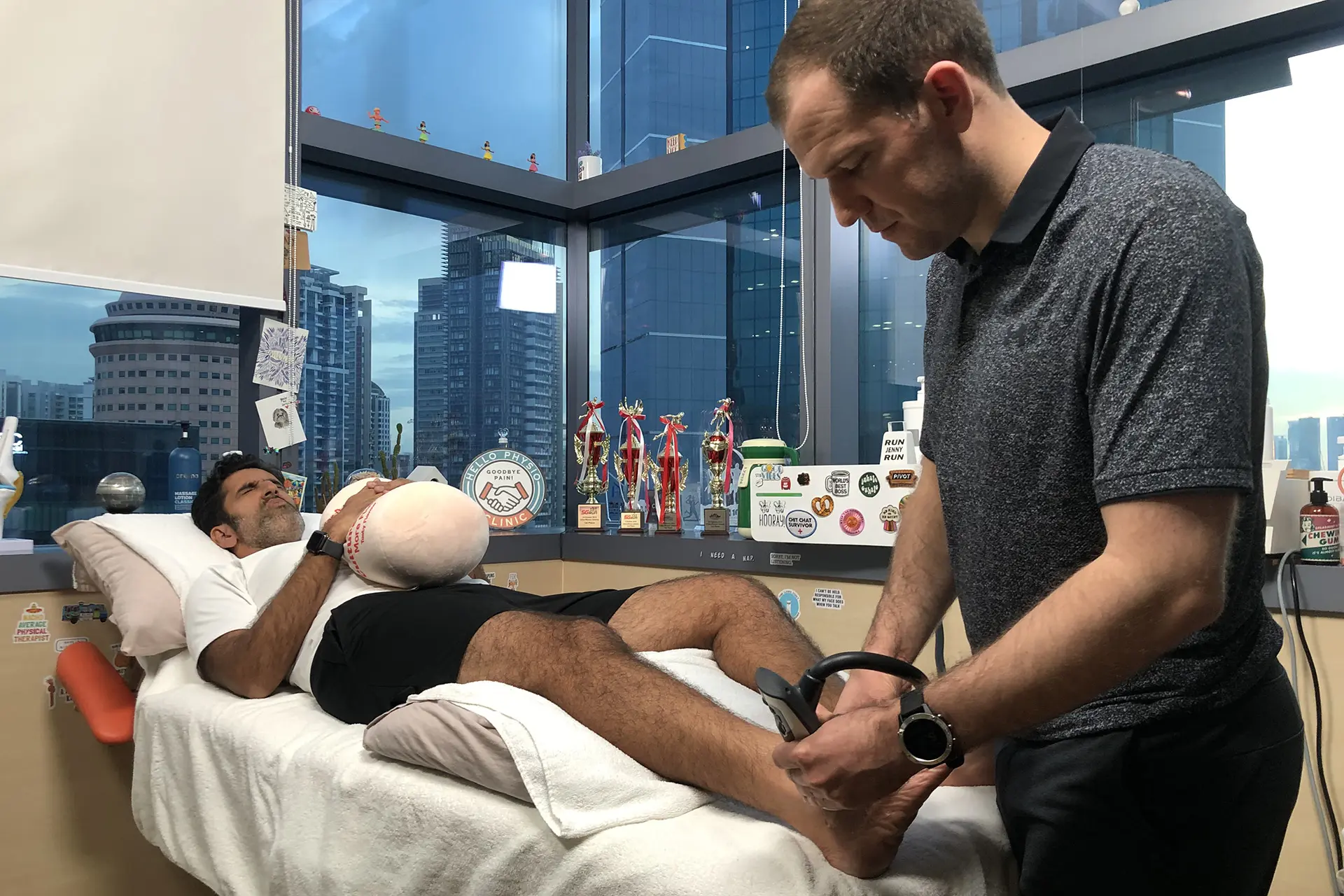
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Physiotherapists use clinical assessments, functional tests and imaging techniques to evaluate the severity and location of the injury. Hamstring strain rehabilitation reduces pain, restores mobility and strengthens the affected muscles.
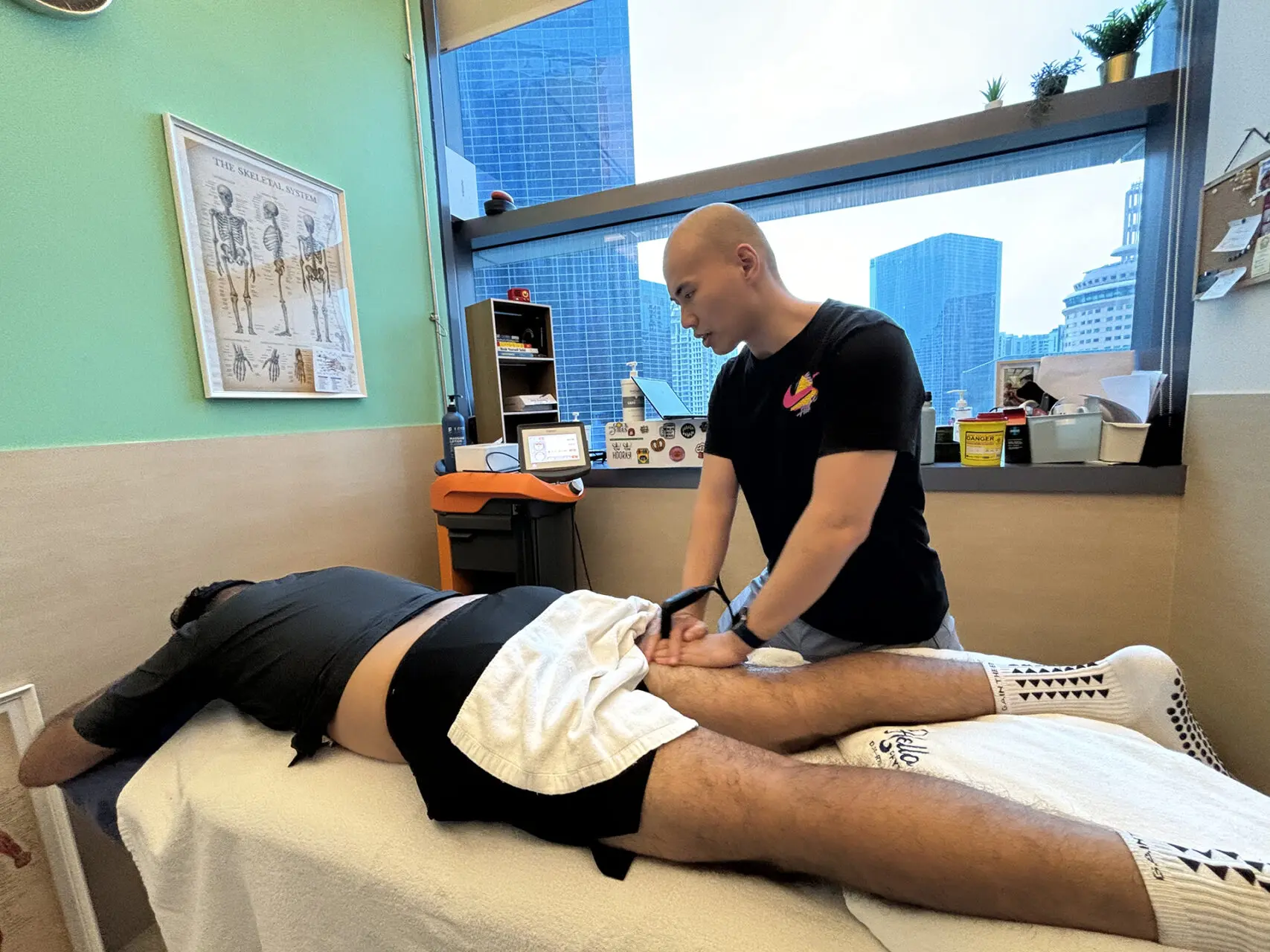
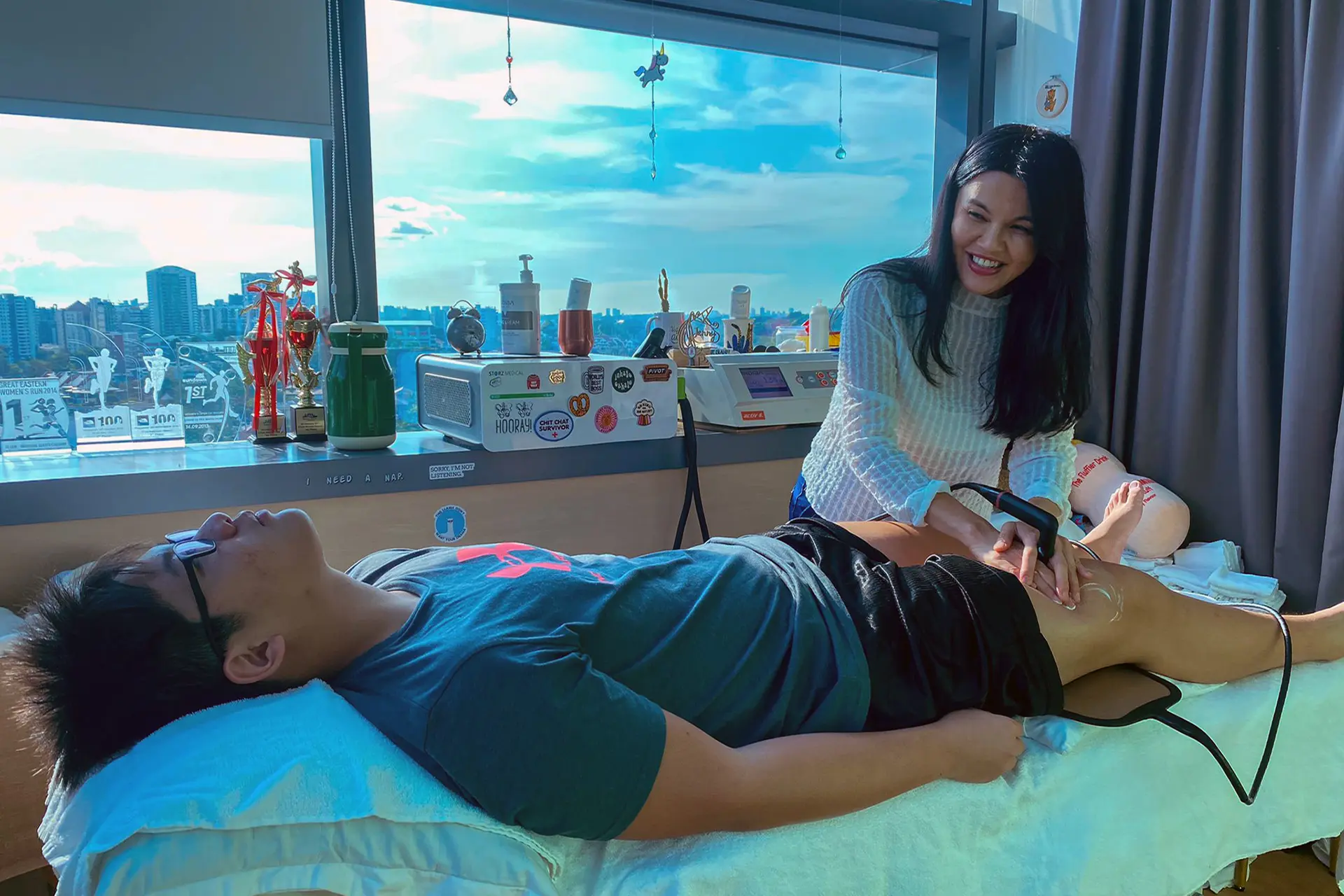
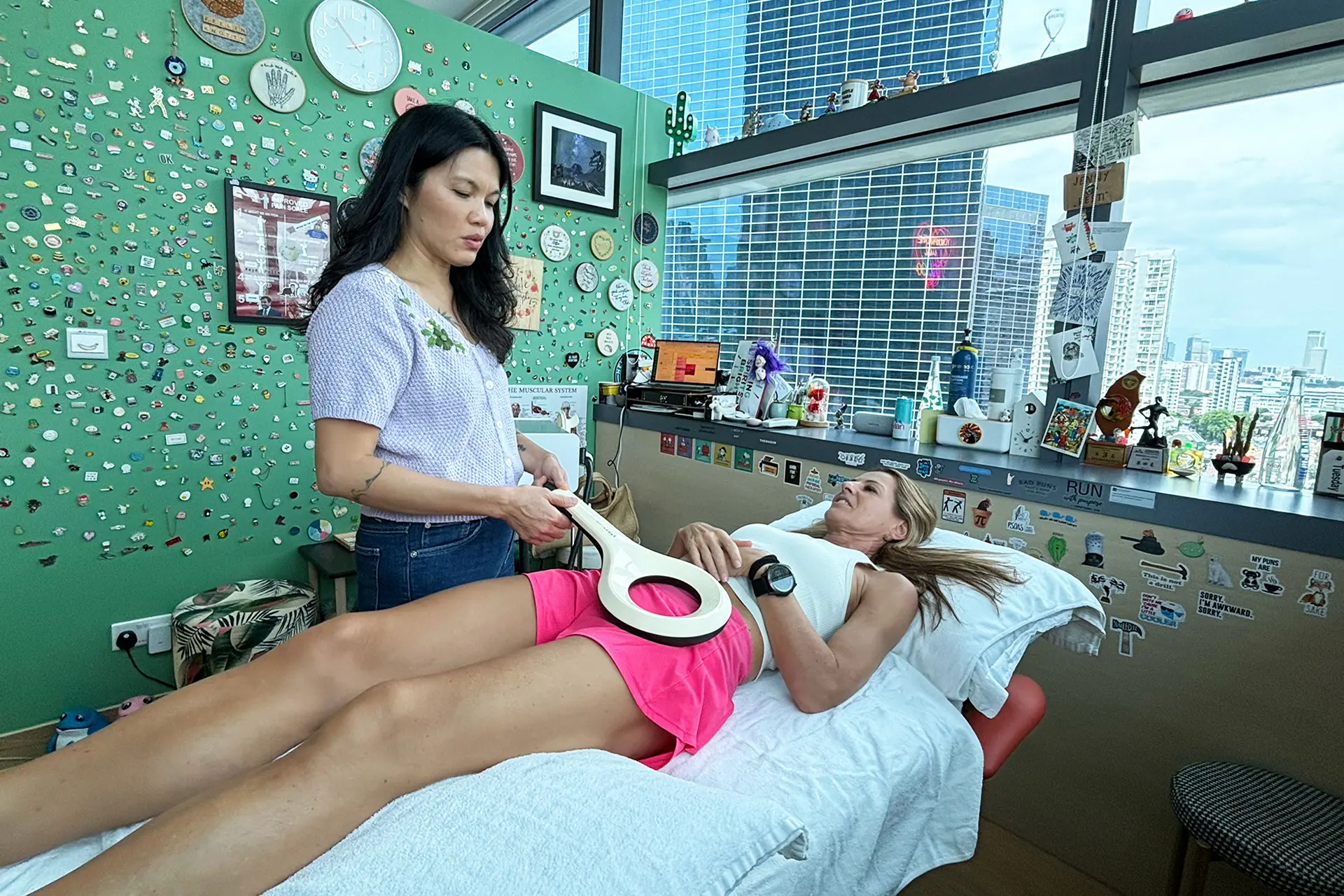
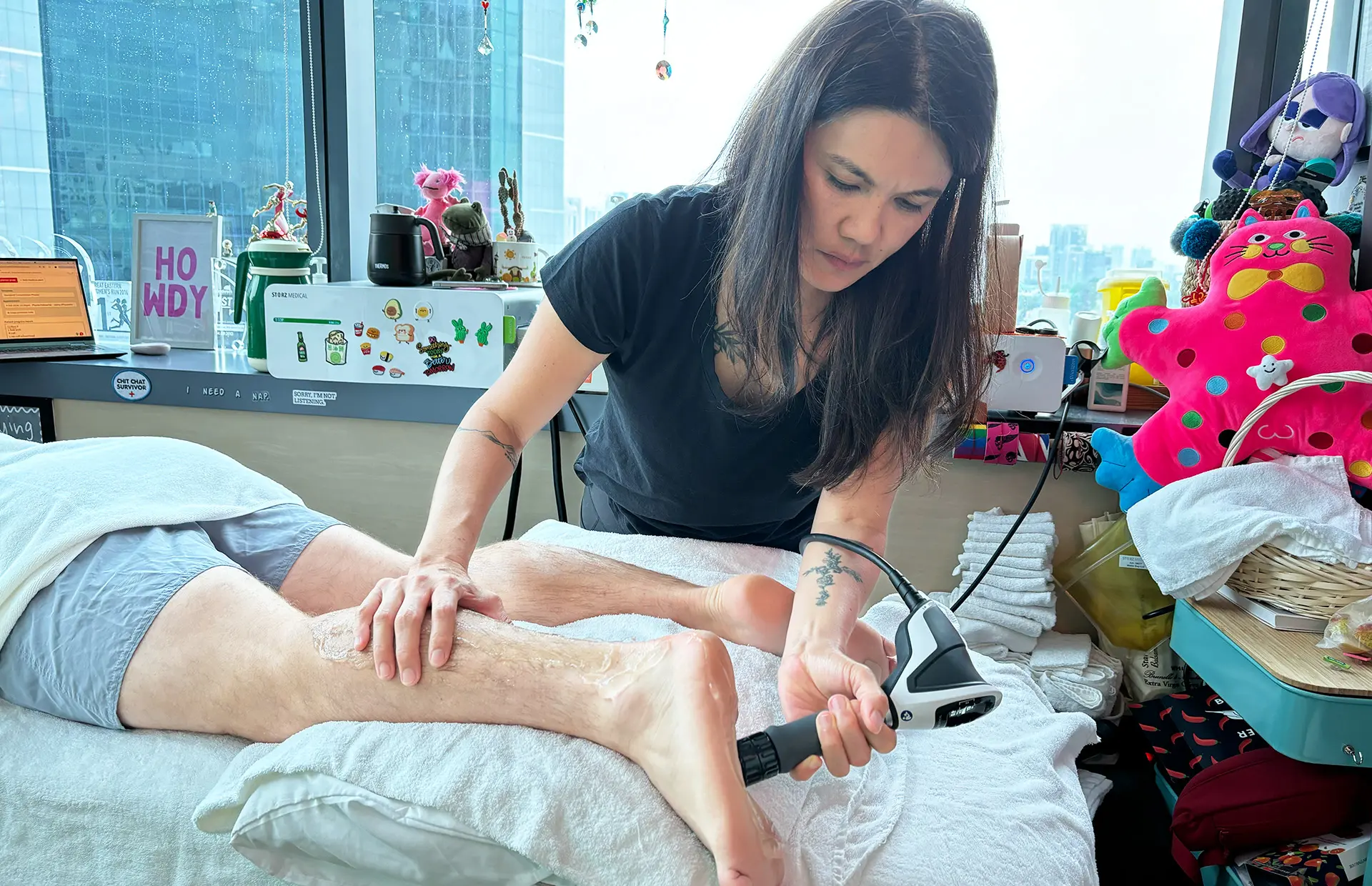
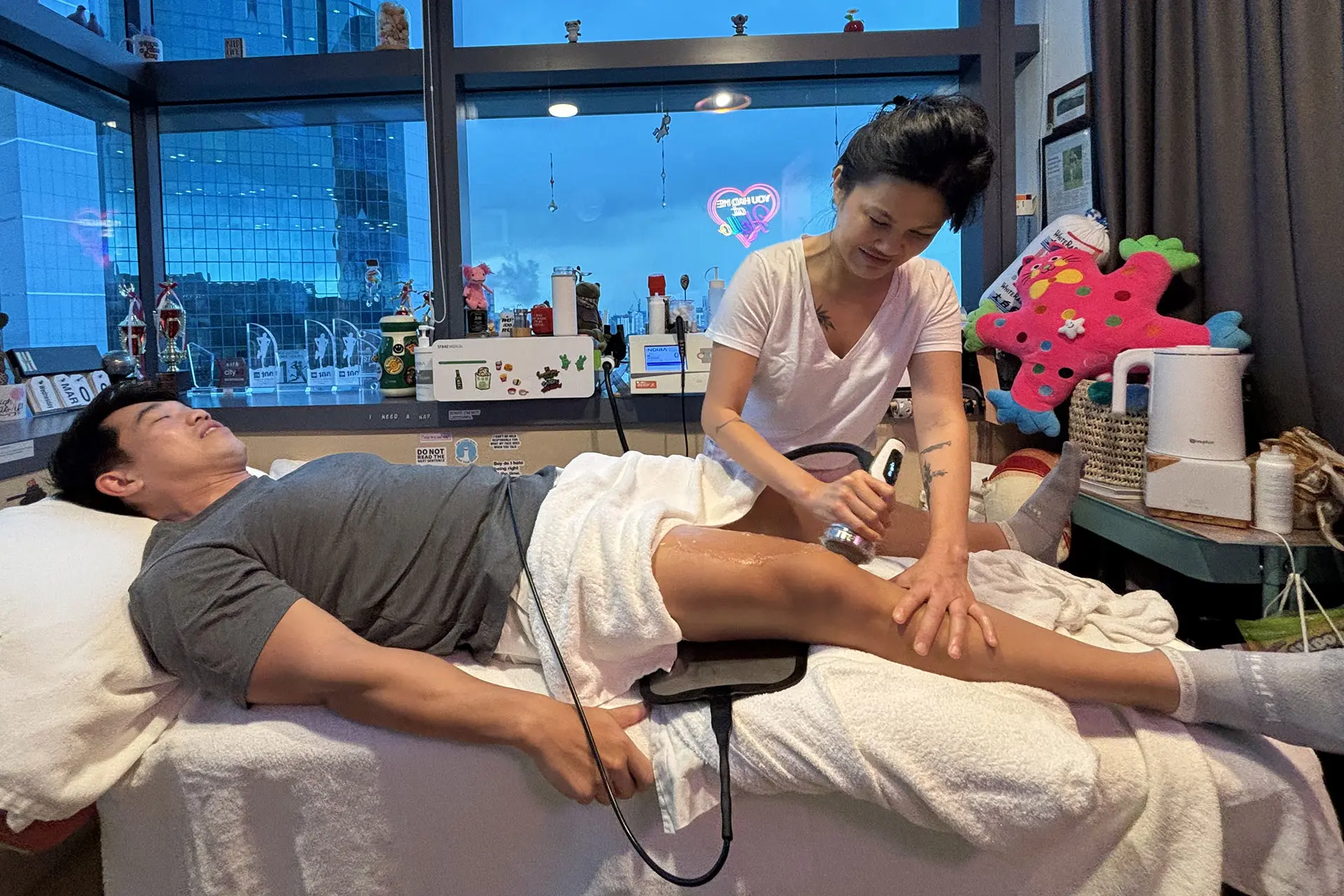
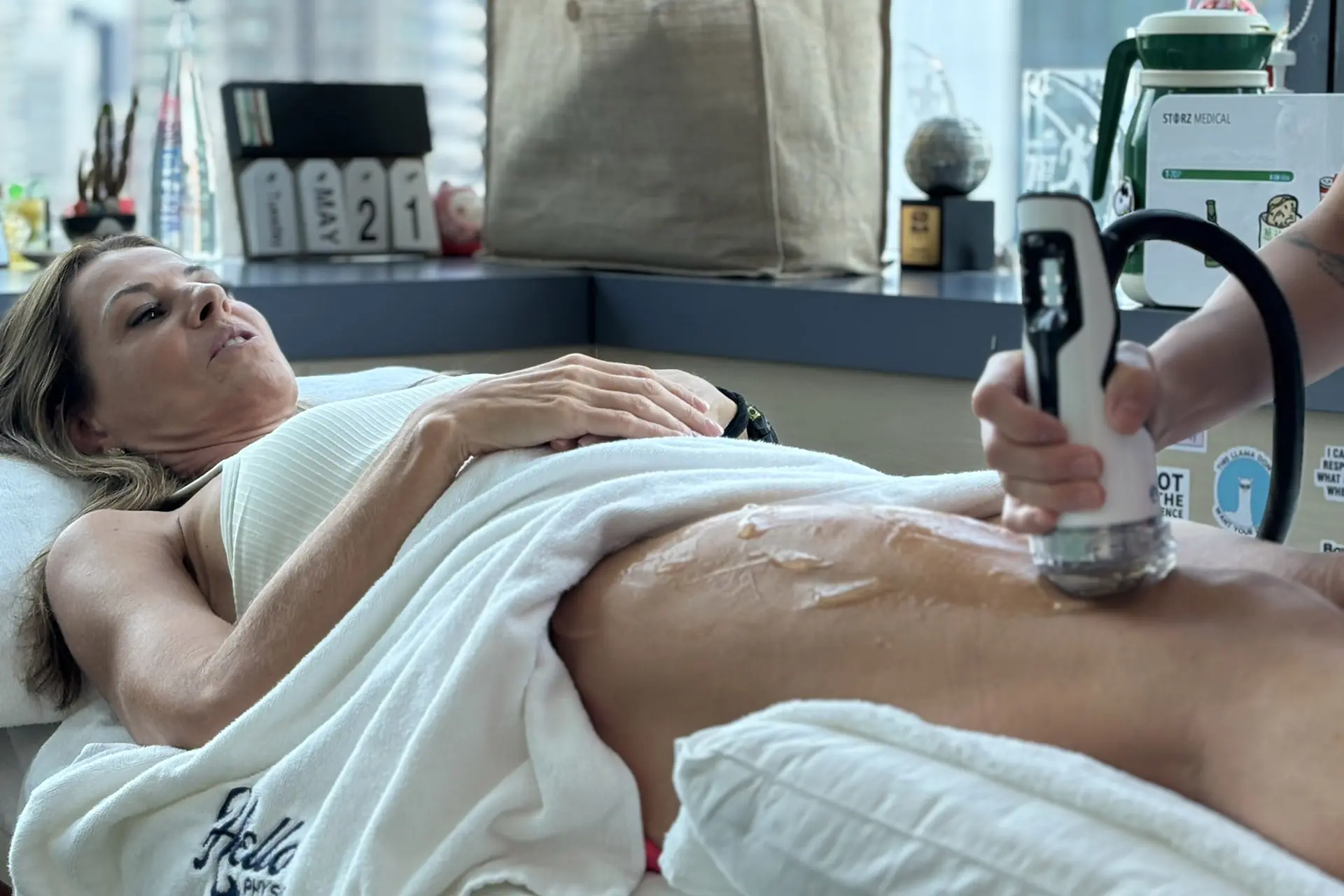
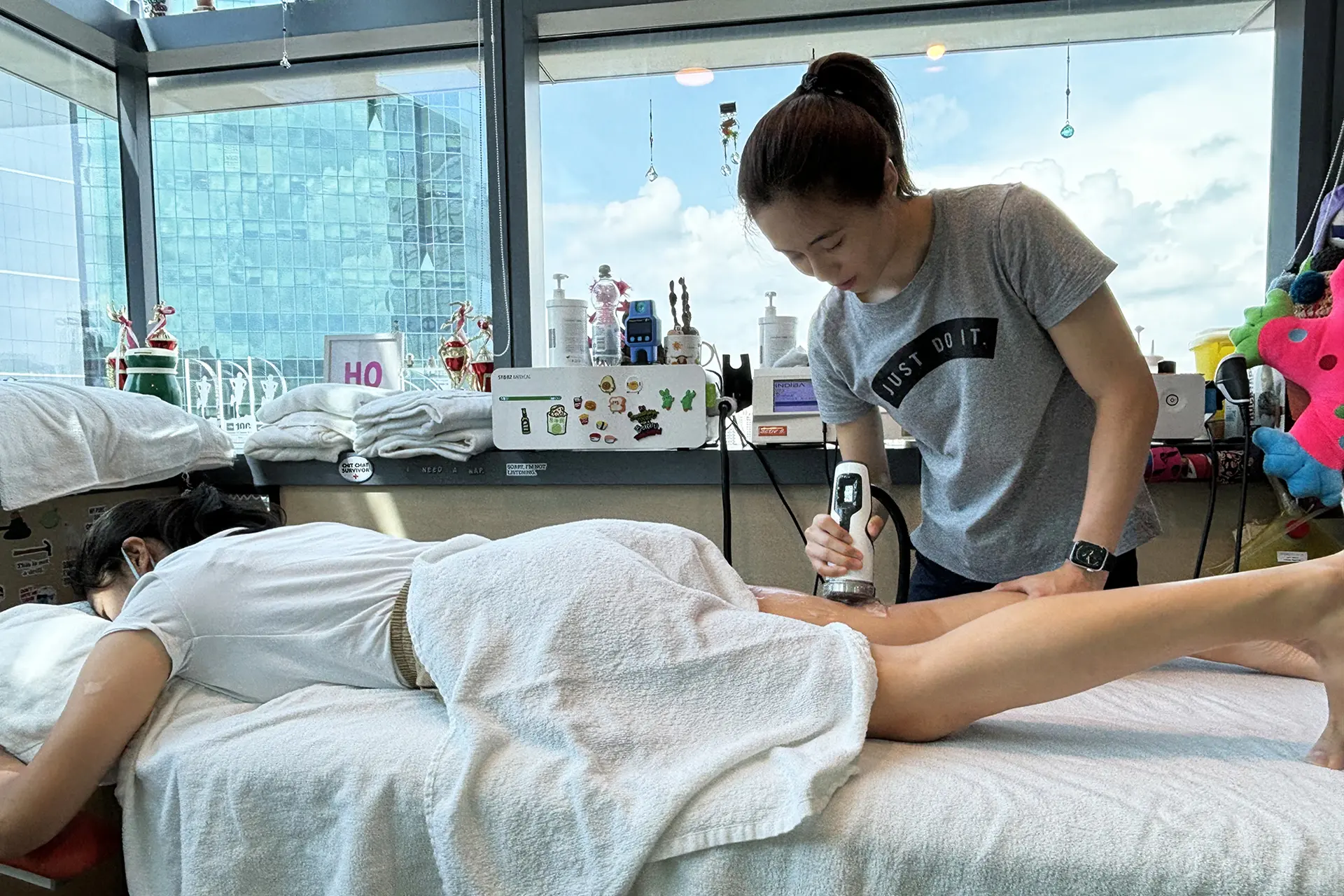
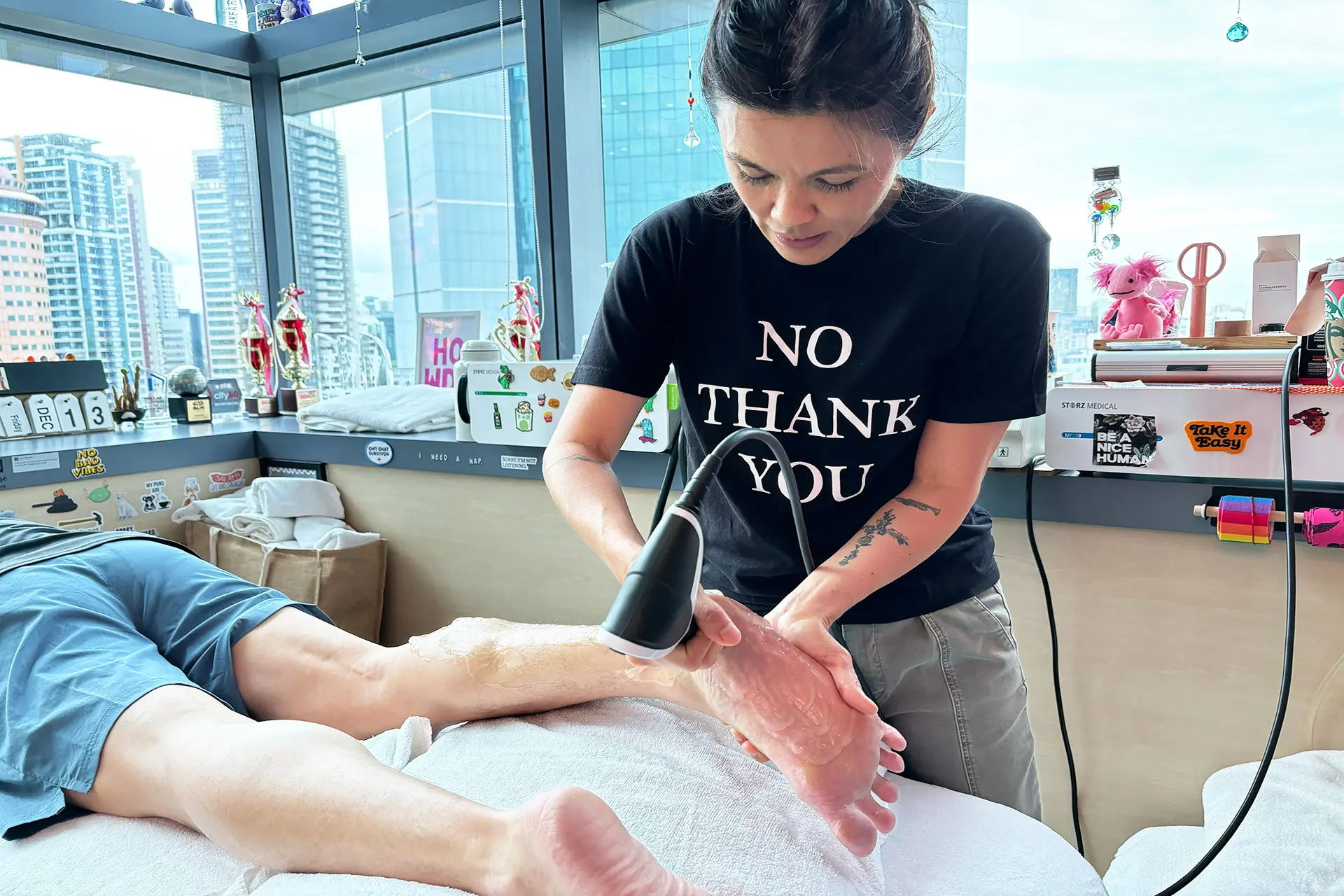
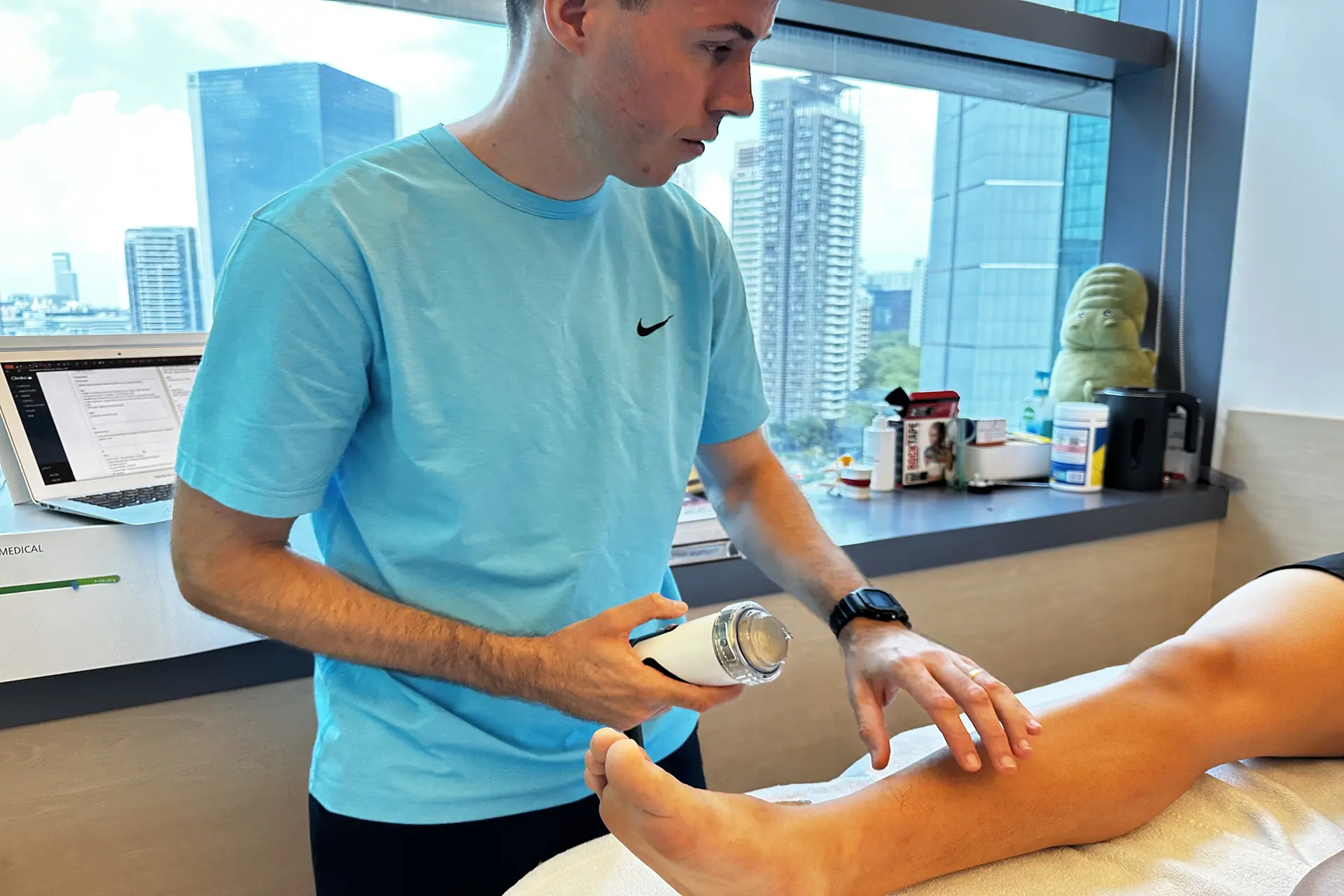
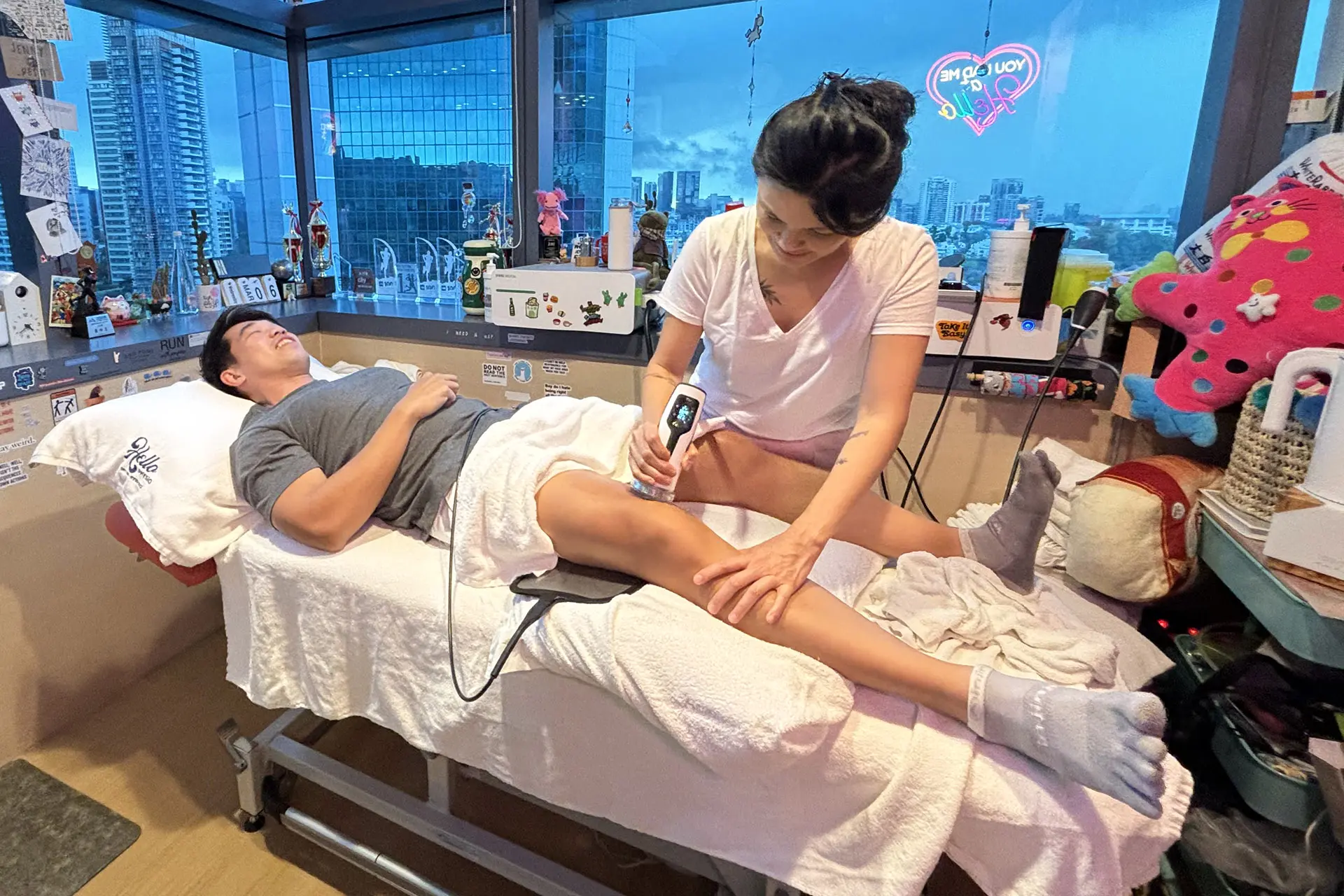
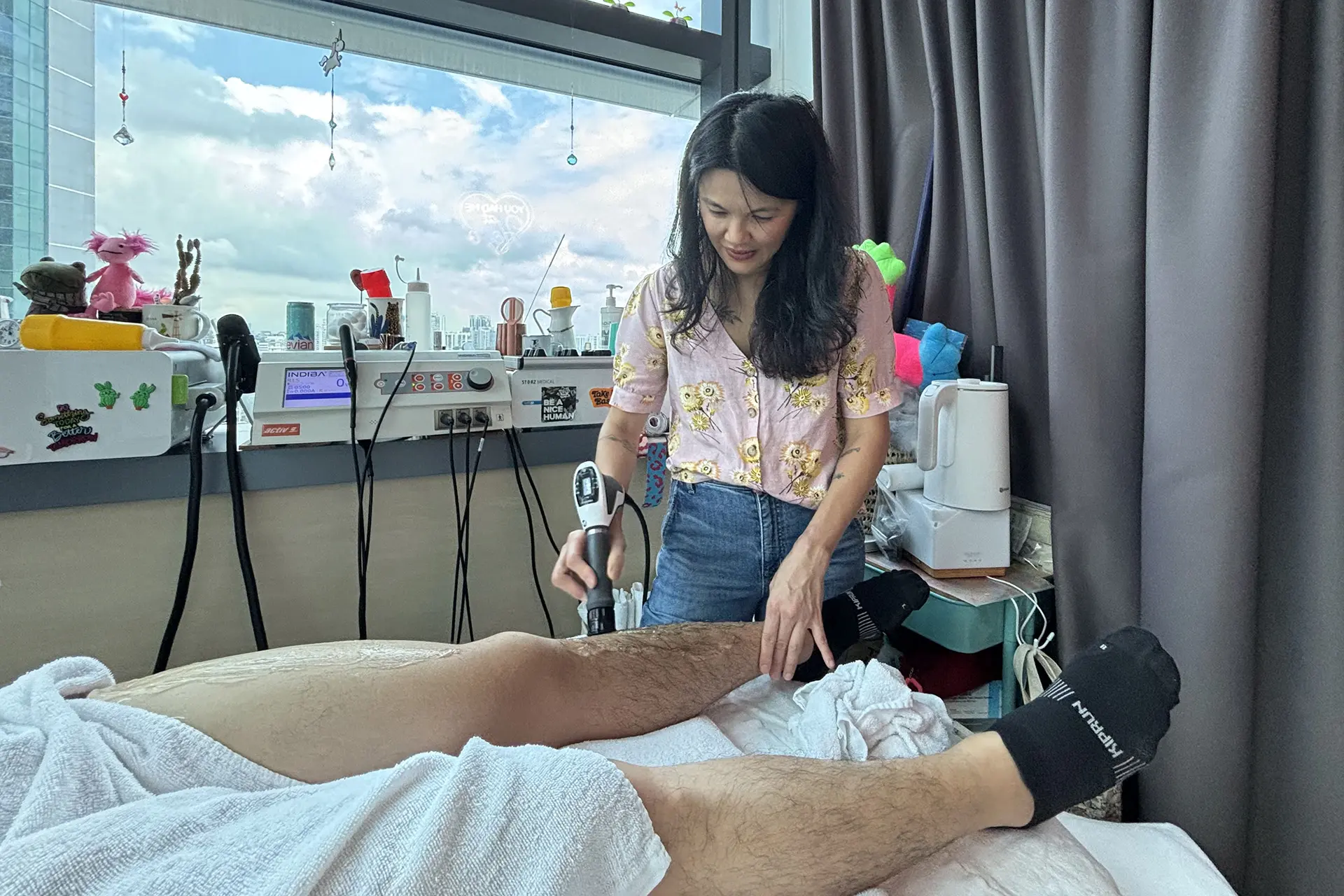
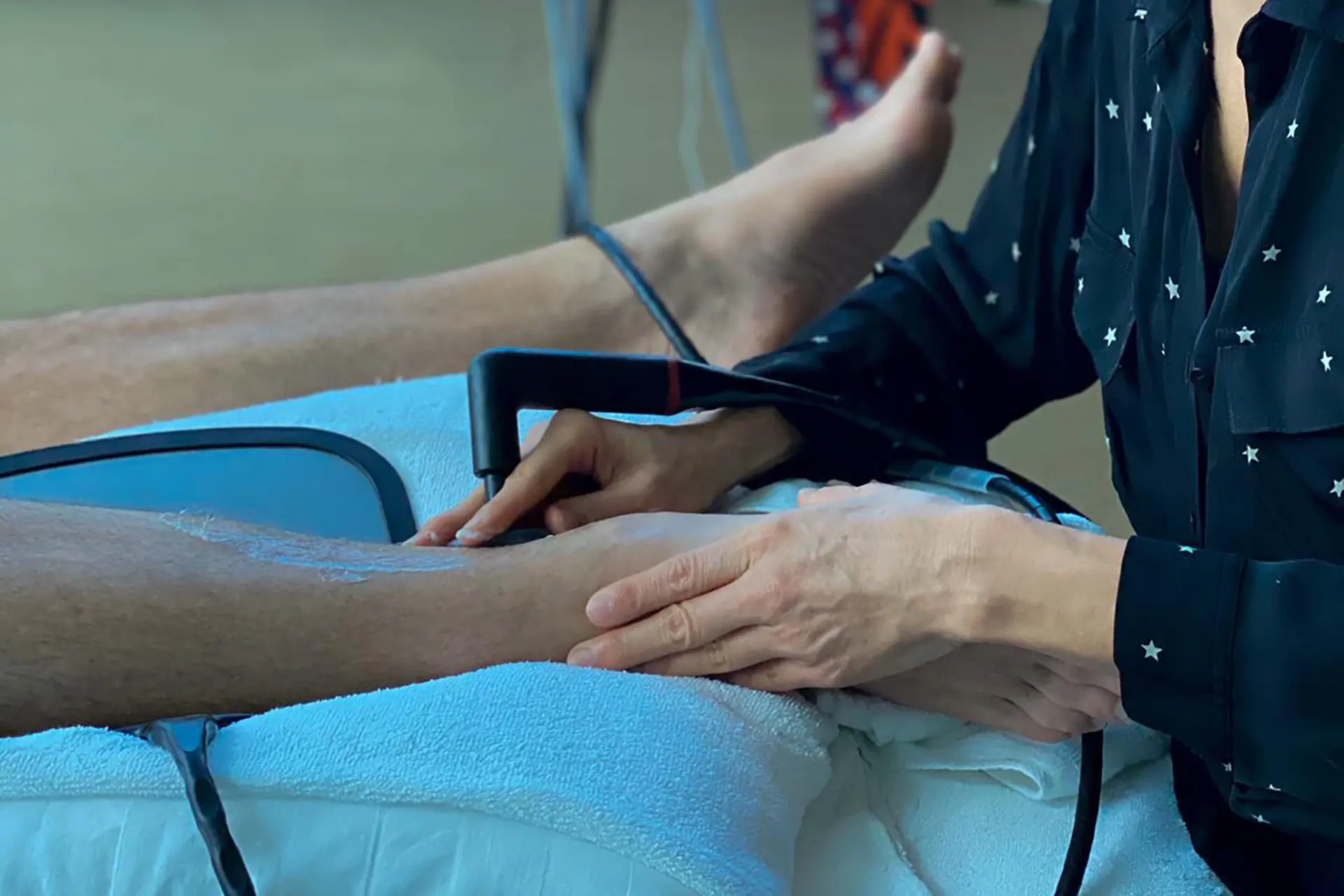
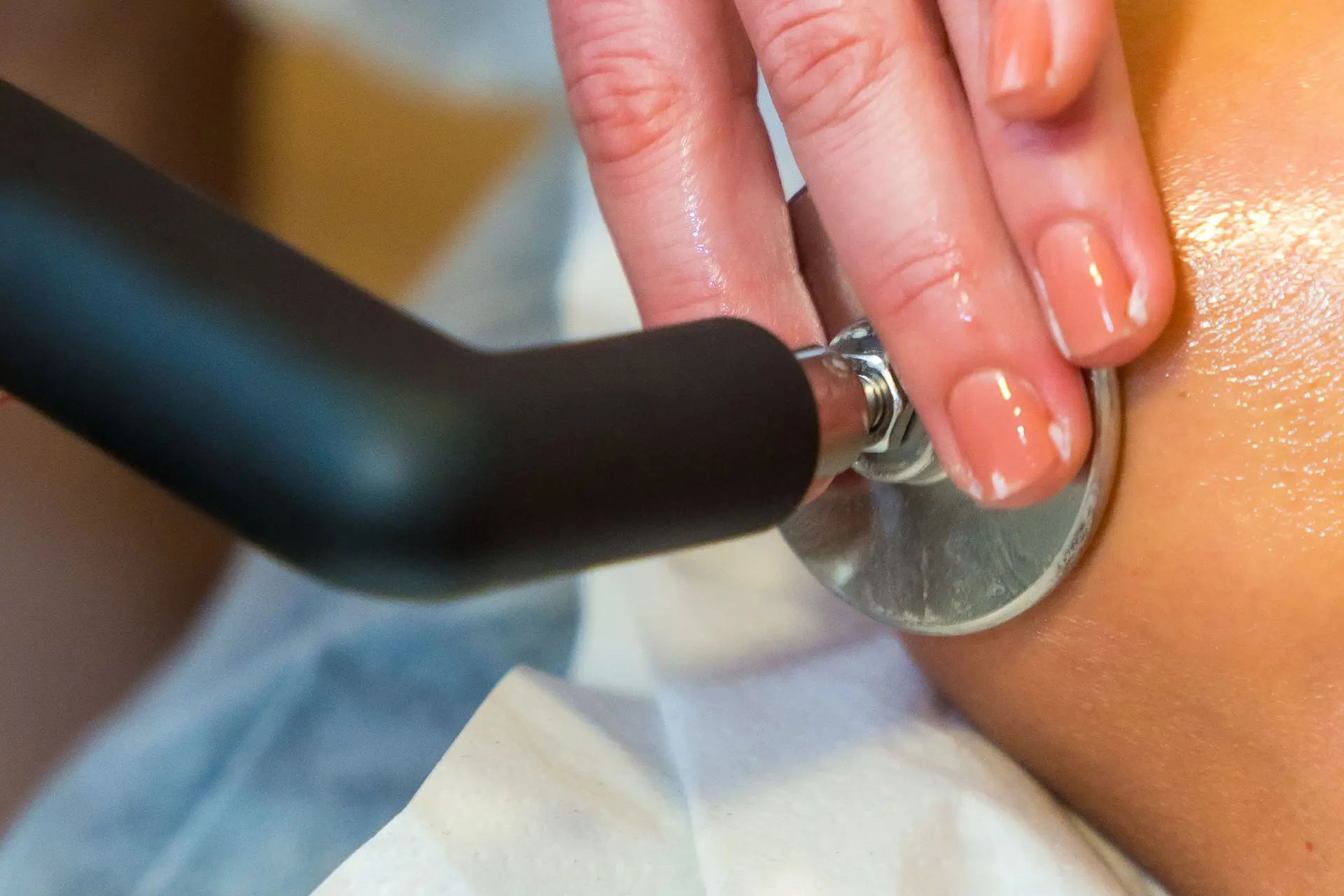
INDIBA® Activ Therapy: This advanced modality uses radiofrequency energy at a specific frequency (448 kHz) to accelerate tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and promote cellular regeneration. INDIBA® Activ works by stimulating ion exchange at the cellular level, which increases ATP production and enhances metabolic activity. This leads to faster repair of damaged muscle fibers and improved blood circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients essential for healing. It also normalises tissue temperature, reduces chronic inflammation and relieves pain by modulating nerve signals. INDIBA® Activ is particularly effective for proximal and upper hamstring strains due to its deep tissue penetration and targeted effects.
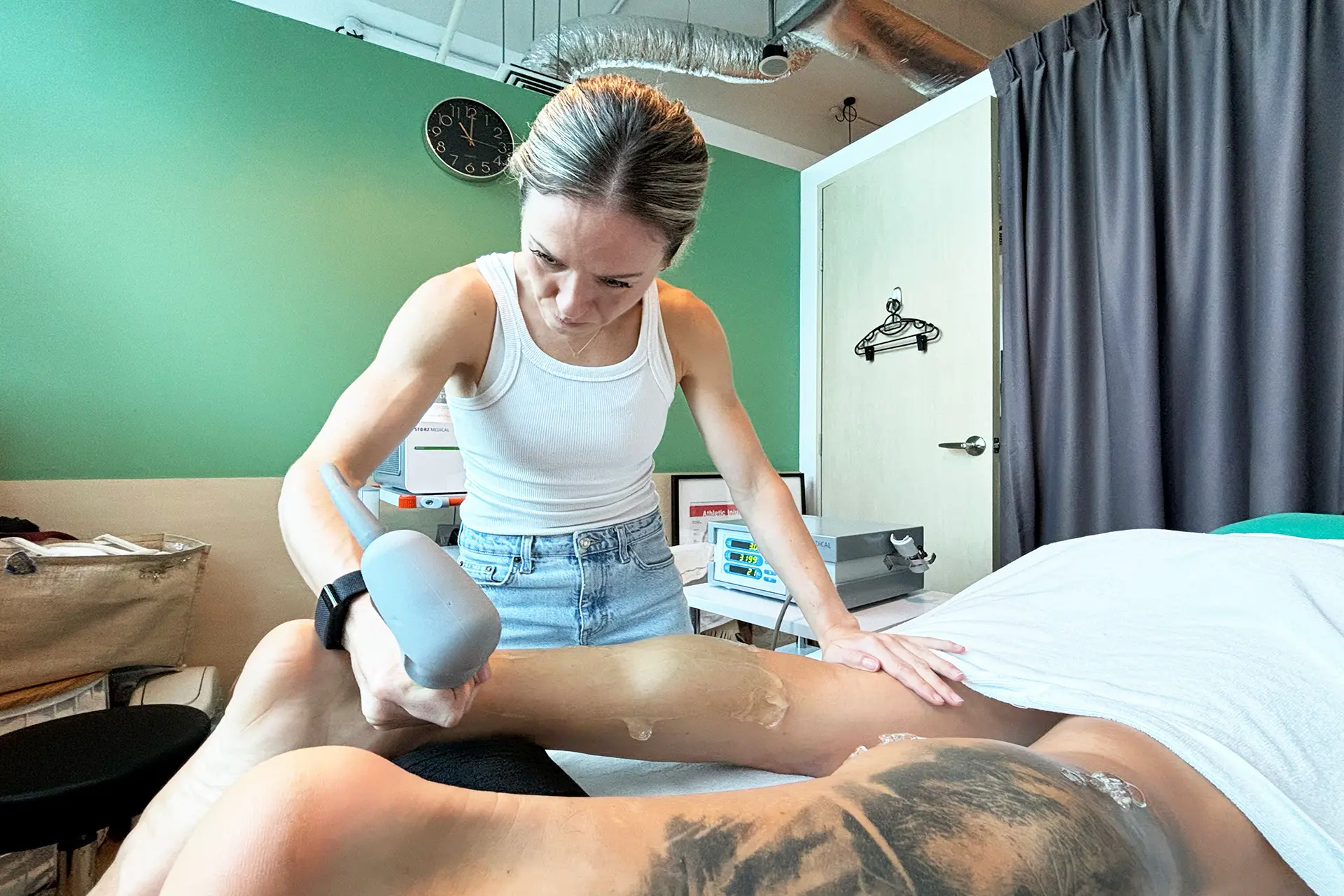
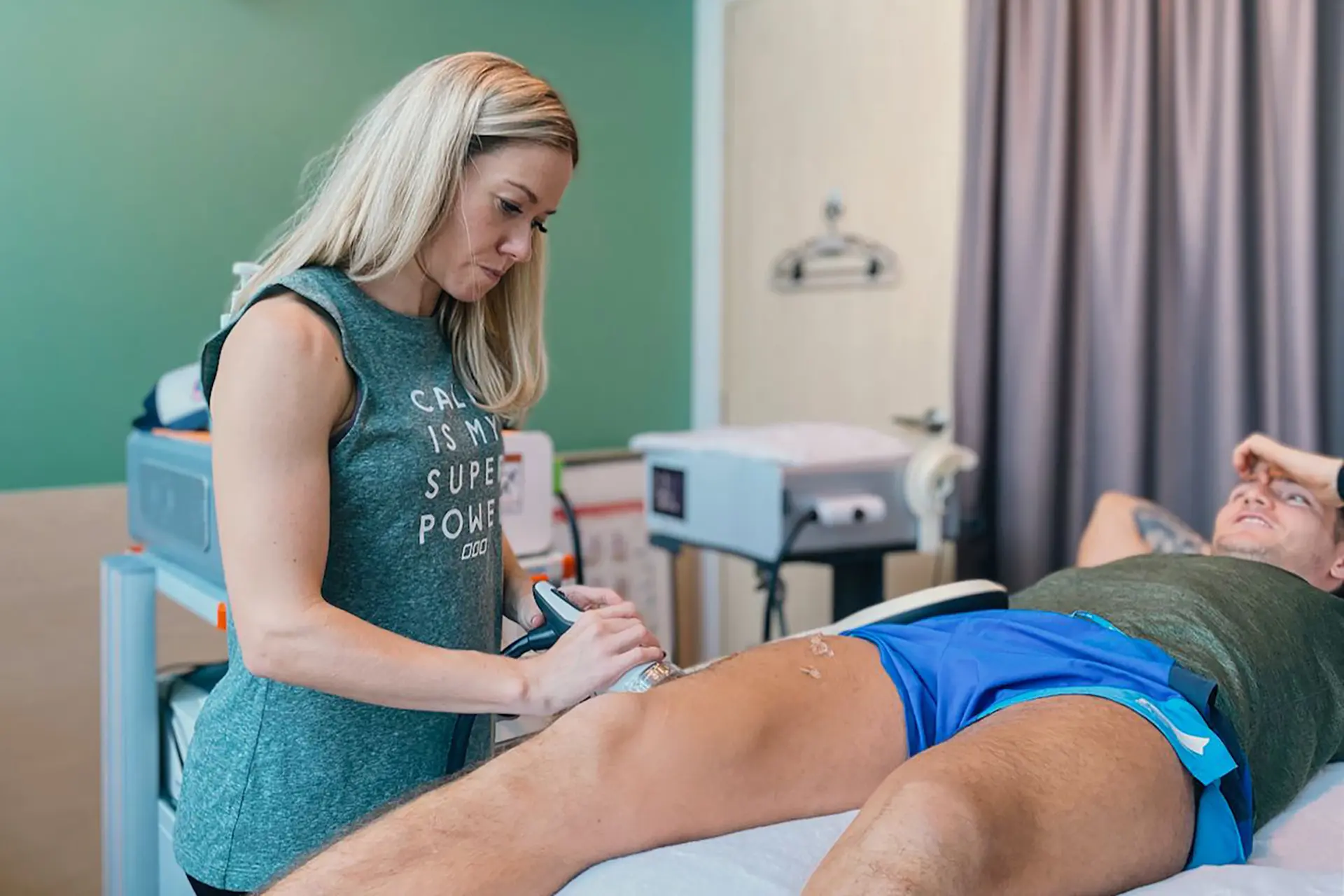
Shockwave Therapy: Shockwave Therapy utilises high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate tissue repair mechanically. This therapy triggers the activation of fibroblasts, which are responsible for collagen production, thereby strengthening the connective tissue in the hamstrings. By promoting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), Shockwave Therapy enhances blood flow to the affected area, accelerating the removal of inflammatory mediators and supporting tissue regeneration. Additionally, it breaks down scar tissue and calcifications, improving flexibility and reducing stiffness, making it particularly effective for moderate to severe hamstring strains.
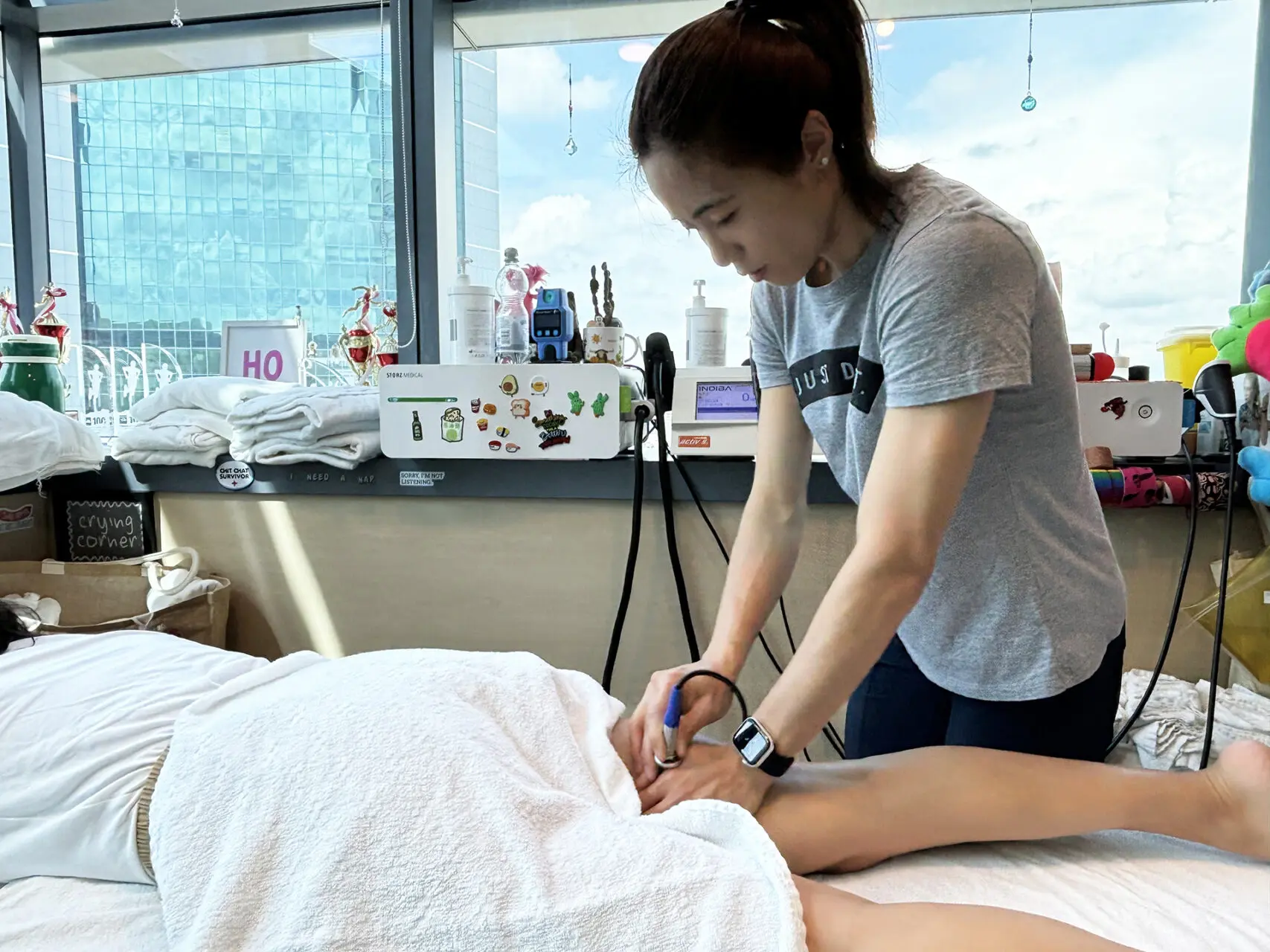
Electromagnetic Transduction Therapy (EMTT): EMTT employs pulsed electromagnetic fields to penetrate deep into the affected tissues, stimulating cellular repair and regeneration. This therapy increases the permeability of cell membranes, facilitating ion exchange and promoting the natural healing process. EMTT also reduces inflammation by modulating inflammatory cytokines and enhances deep tissue repair by improving mitochondrial function. Its ability to reach deeper layers of tissue makes it an ideal adjunctive treatment for severe hamstring strains, ensuring comprehensive recovery and long-term muscle health.
Hamstring Strain Stretches and Exercises
Stretching and strengthening exercises are integral to hamstring strain injury rehabilitation. Physiotherapists design customized programs that include examples such as:

- Standing Hamstring Stretch: Stand upright with one leg extended straight forward, resting on a low surface, and gently reach toward the toes to stretch the back of the thigh.
- Seated Forward Bend: Sit with both legs extended forward and slowly lean toward your feet, keeping your back straight, to improve hamstring flexibility.
- Hamstring Bridge Exercise: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground. Lift your hips upward while engaging your hamstrings and glutes to build strength.
- Dynamic Leg Swings: Swing one leg forward and backward in a controlled manner to gently stretch and prepare the hamstrings for activity.
- Controlled Lunges: Perform slow, deep lunges to enhance flexibility, strength, and coordination, gradually progressing intensity as the injury heals.
Hamstring strain injuries can disrupt daily life and athletic performance, but recovery is achievable with proper care and physiotherapy. HelloPhysio’s expertise in advanced treatments like INDIBA® Activ, Shockwave Therapy and EMTT ensures patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their needs.
Whether addressing a Grade 1 strain or navigating the complexities of a proximal hamstring strain, our team provides the guidance and tools necessary for effective recovery. Contact HelloPhysio today.