|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Medial collateral ligament (MCL) sprains are a common knee ligament injury, particularly in athletes and people who make sudden twisting motions, or experience a direct impact on the knee. The MCL is a crucial stabilizing ligament located on the knee’s inner side, helping prevent excessive side-to-side movement. When overstretched or torn, a medial collateral ligament sprain can significantly affect knee function and mobility.
Fortunately, physiotherapy can help to accelerate recovery, reduce pain, and restore knee strength after an MCL sprain. Complementary therapies like Shockwave Therapy and INDIBA® further enhance healing, making them valuable tools in MCL sprain rehabilitation.
Understanding MCL Sprains Causes and Risk Factors
MCL injuries can occur for various reasons, including direct blows to the outside of the knee, causing the ligament to stretch or tear. A knee ligament sprain, particularly an MCL sprain, typically occurs due to excessive valgus force, meaning a direct impact or pressure on the outer part of the knee, causing the ligament on the inner side to stretch or tear.
Sudden twisting or bending of the knee, often seen in high-impact sports like football, soccer, tennis and basketball, can also lead to MCL injuries. This injury frequently happens in contact sports but can also occur from accidental falls or abrupt changes in movement as well.
Other than athletes participating in high-impact sports, people with poor knee alignment or biomechanics and weak or imbalanced thigh muscles are more prone to MCL injuries. Over time, wear and tear of the ligament can weaken the MCL, making it more susceptible to injury.
Lifting heavy objects repeatedly can also cause stress and pressure on the MCL ligament. Individuals with a history of knee injuries or surgeries are at a higher risk, as are older adults, whose ligaments tend to weaken with age.
Most MCL injuries do not require surgery due to the ligament’s good blood supply, which aids natural healing. Still, physiotherapy can support and bolster the natural recovery process from an MCL injury.

MCL Sprain Symptoms
Recognizing MCL sprain symptoms early ensures timely intervention. Common indicators include:
- Pain and tenderness along the inner side of the knee
- Swelling around the injured area
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Instability or a feeling of the knee “giving way” when walking or turning
- Pain when bending or extending the knee
Classification of MCL Sprains
MCL sprains are graded based on the degree of ligament damage:
- Grade 1 (Mild): Slight overstretching with micro-tearing; minimal pain and swelling
- Grade 2 (Moderate): Partial tear; noticeable pain, swelling, and mild knee instability
- Grade 3 (Severe): Complete tear; significant pain, swelling, and knee instability
Identifying the severity of the injury helps determine MCL sprain recovery time. Milder cases heal within a few weeks, while severe MCL tears may require months of rehabilitation.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing an MCL injury typically starts with a thorough physical examination and subsequent imaging tests, such as X-rays or an MRI. During the examination, a physiotherapist will assess the knee’s stability and range of motion to determine the severity of the injury. Imaging tests help visualize the extent of the damage to the MCL and any associated knee injuries.
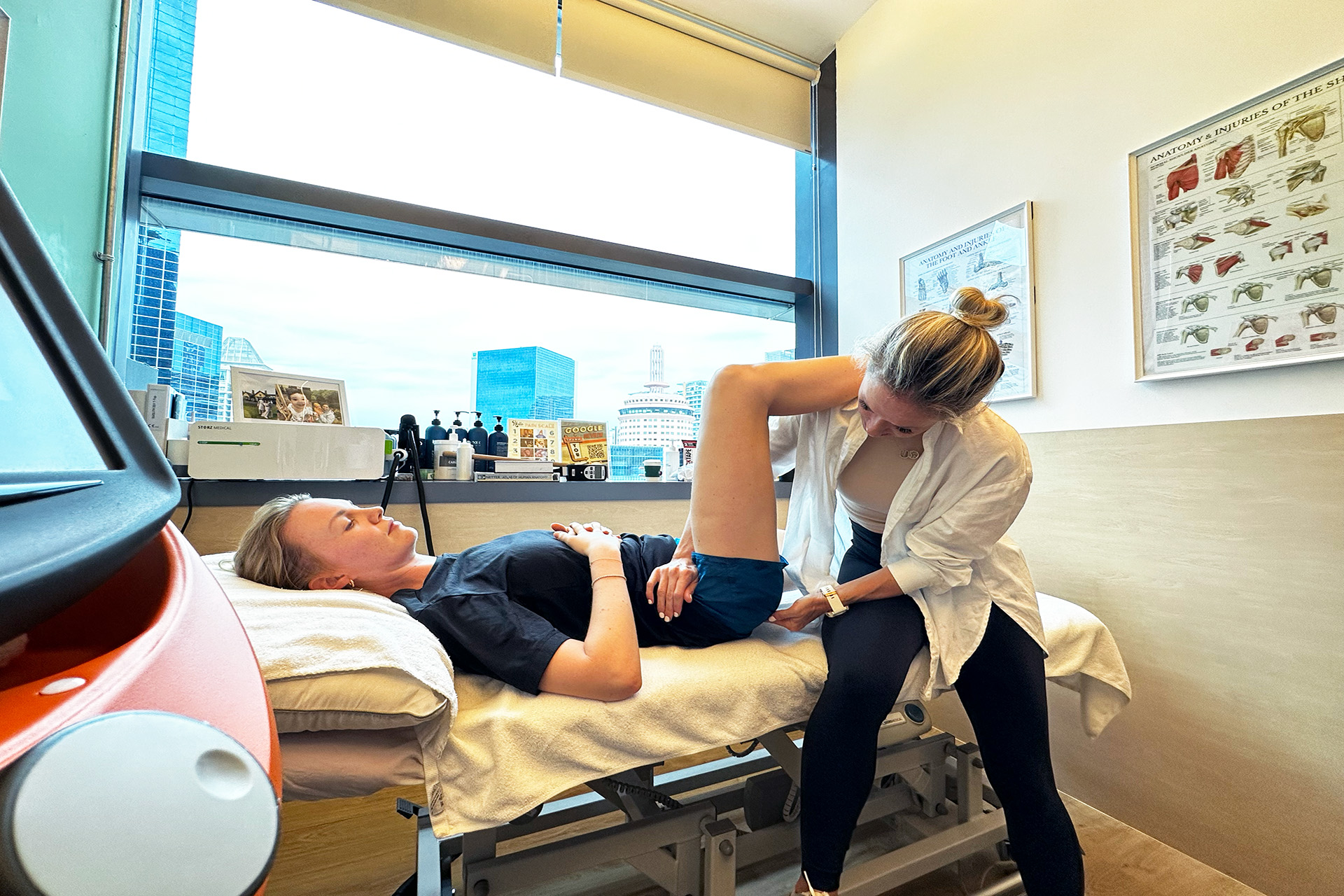
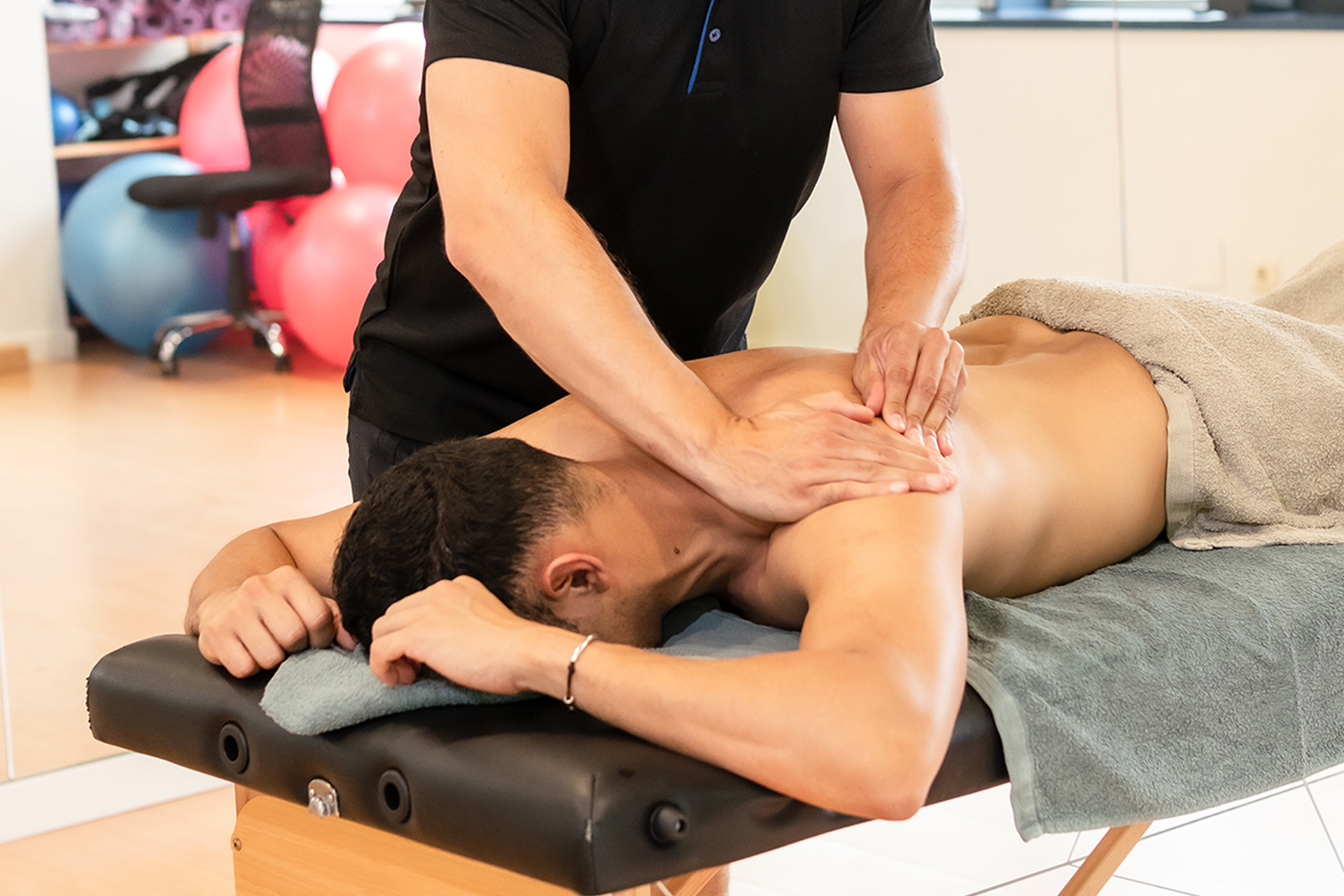
Treatment for MCL injuries usually involves a combination of conservative and, in some cases, surgical approaches. Physical therapy improves strength, flexibility and range of motion. A knee brace can provide additional support and stability to the injured knee while it recovers. A comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual’s condition ensures optimal recovery and return to normal activities.
Pain management medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort. In severe cases with a complete tear or significant instability, surgery may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the MCL. One option is a graft, created using tissue from either elsewhere in the patient’s body, or a donor.
How to Recover from an MCL Sprain
The key to recovering from an MCL sprain effectively lies in a structured rehabilitation program tailored to your condition. Physiotherapy ensures safe and progressive recovery by addressing pain, strengthening muscles, and restoring knee function.
Acute Phase: Initial MCL Sprain Treatment At Home
During the first few days following an MCL sprain, immediate care focuses on reducing pain and inflammation. The PEACE and LOVE protocol is now preferred over traditional RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) to facilitate optimal healing. PEACE (Protection, Elevation, Avoid anti-inflammatories, Compression, Education) is applied in the acute phase to control swelling and limit further damage. LOVE (Load, Optimism, Vascularization, Exercise) is the long-term guide to rehabilitation by gradually reintroducing movement to prevent stiffness, encouraging tissue healing, and strengthening post MCL sprain.
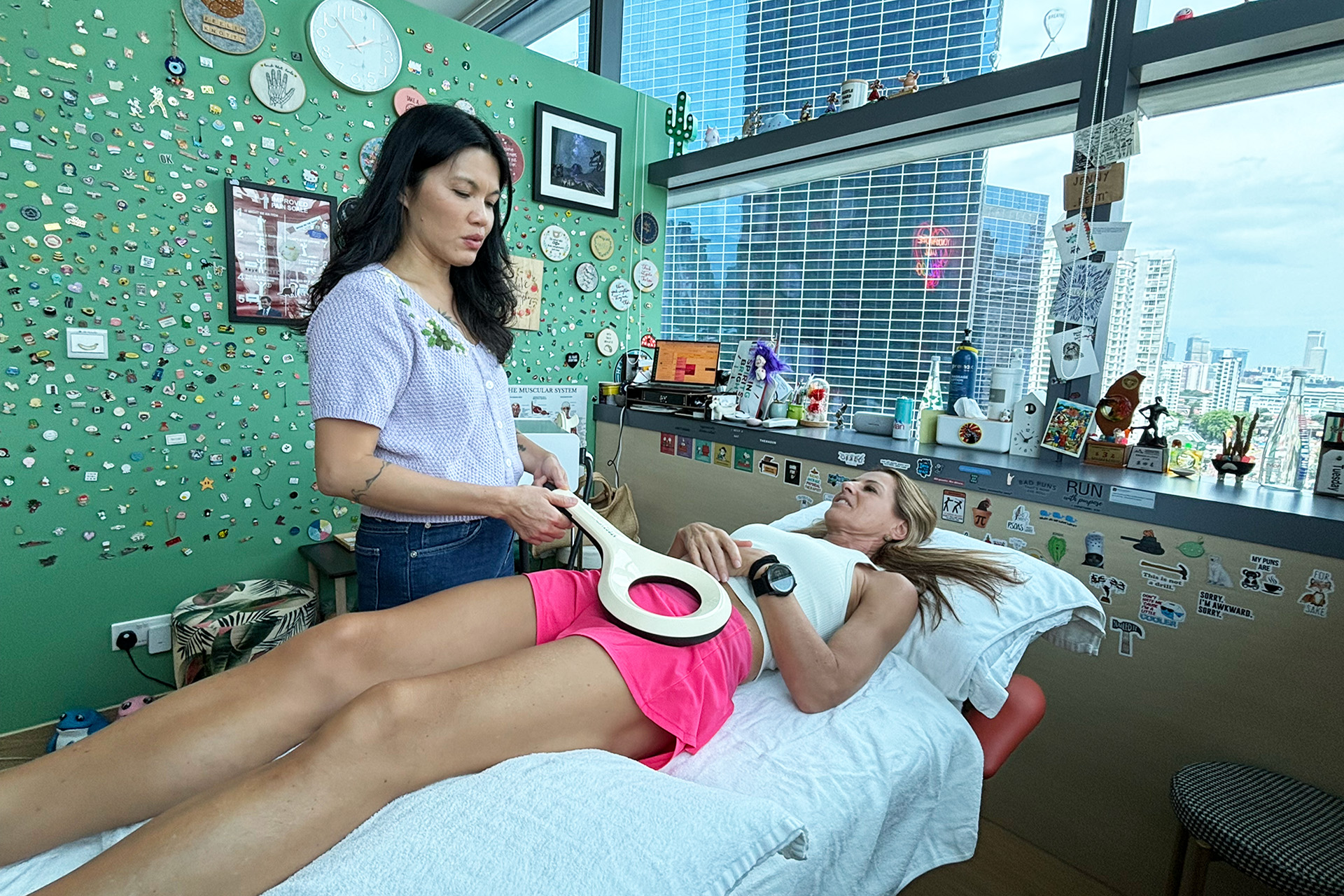
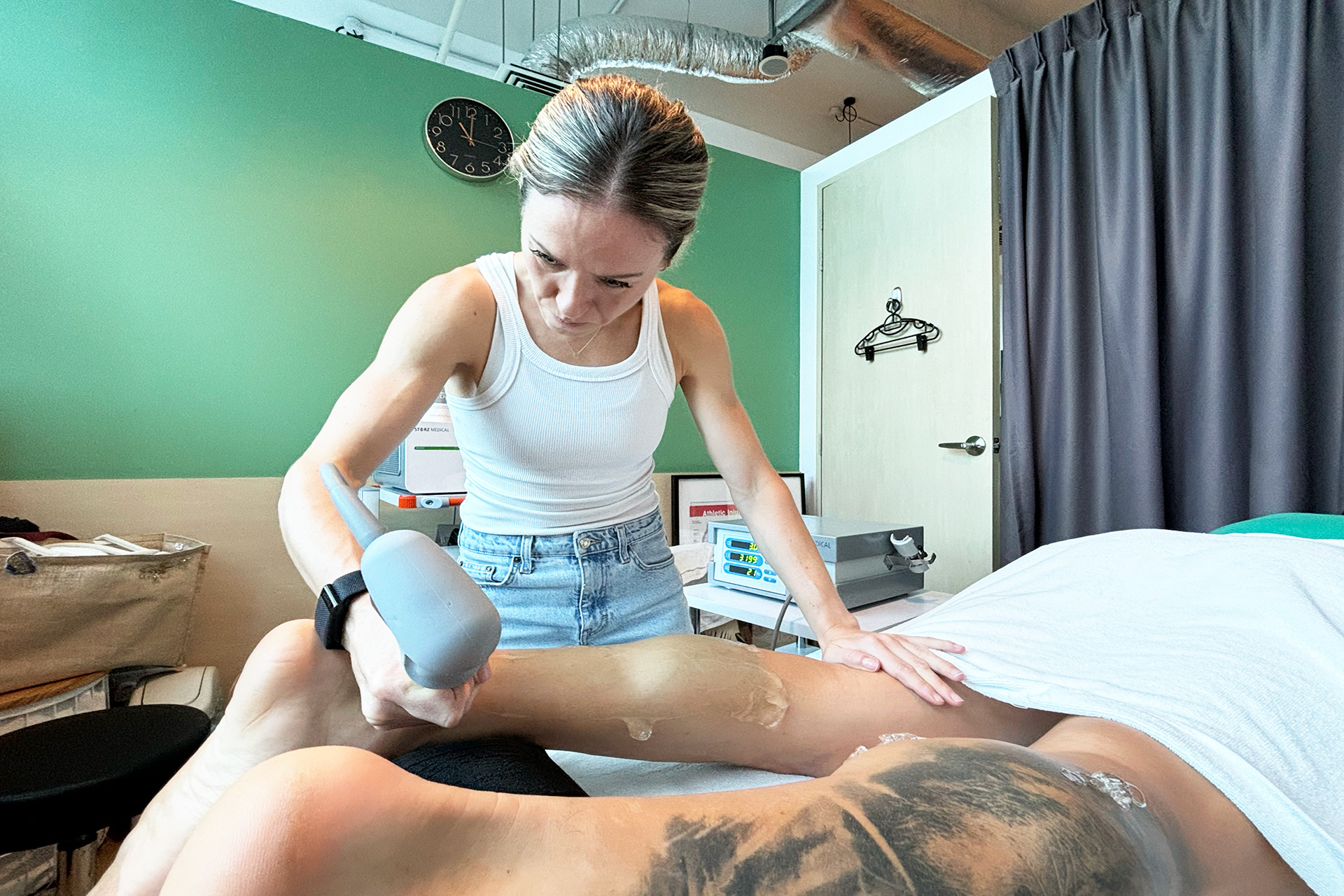
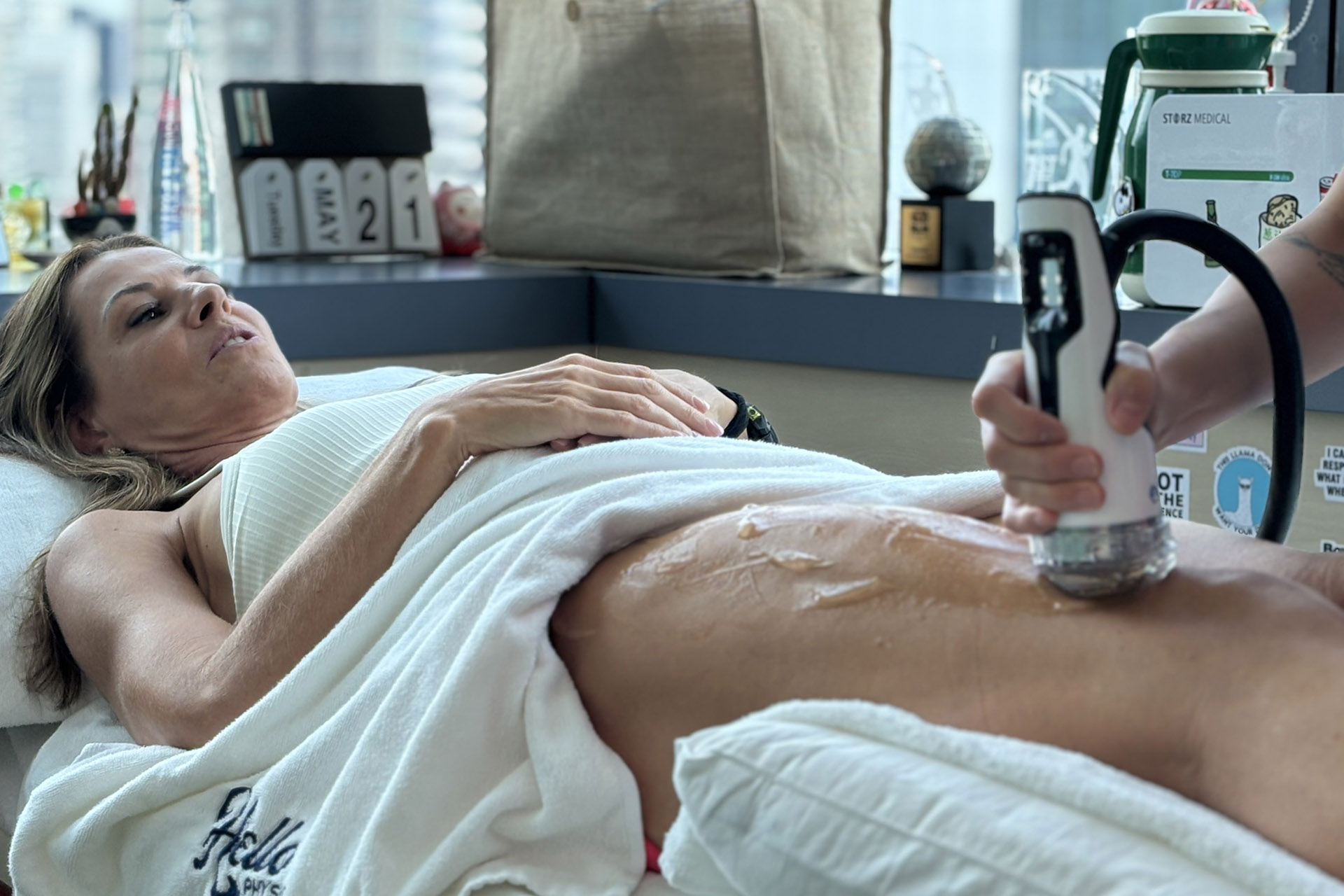
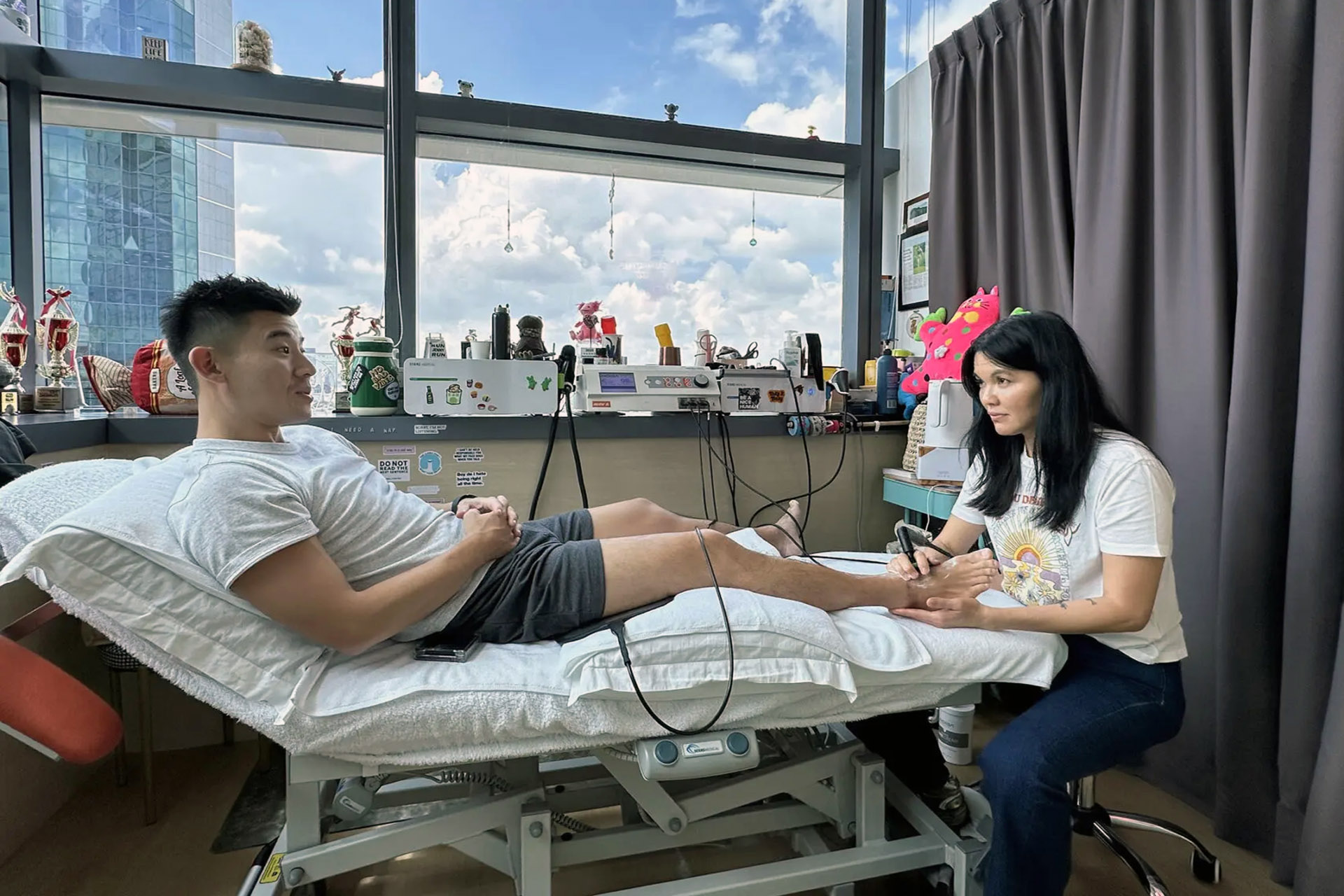
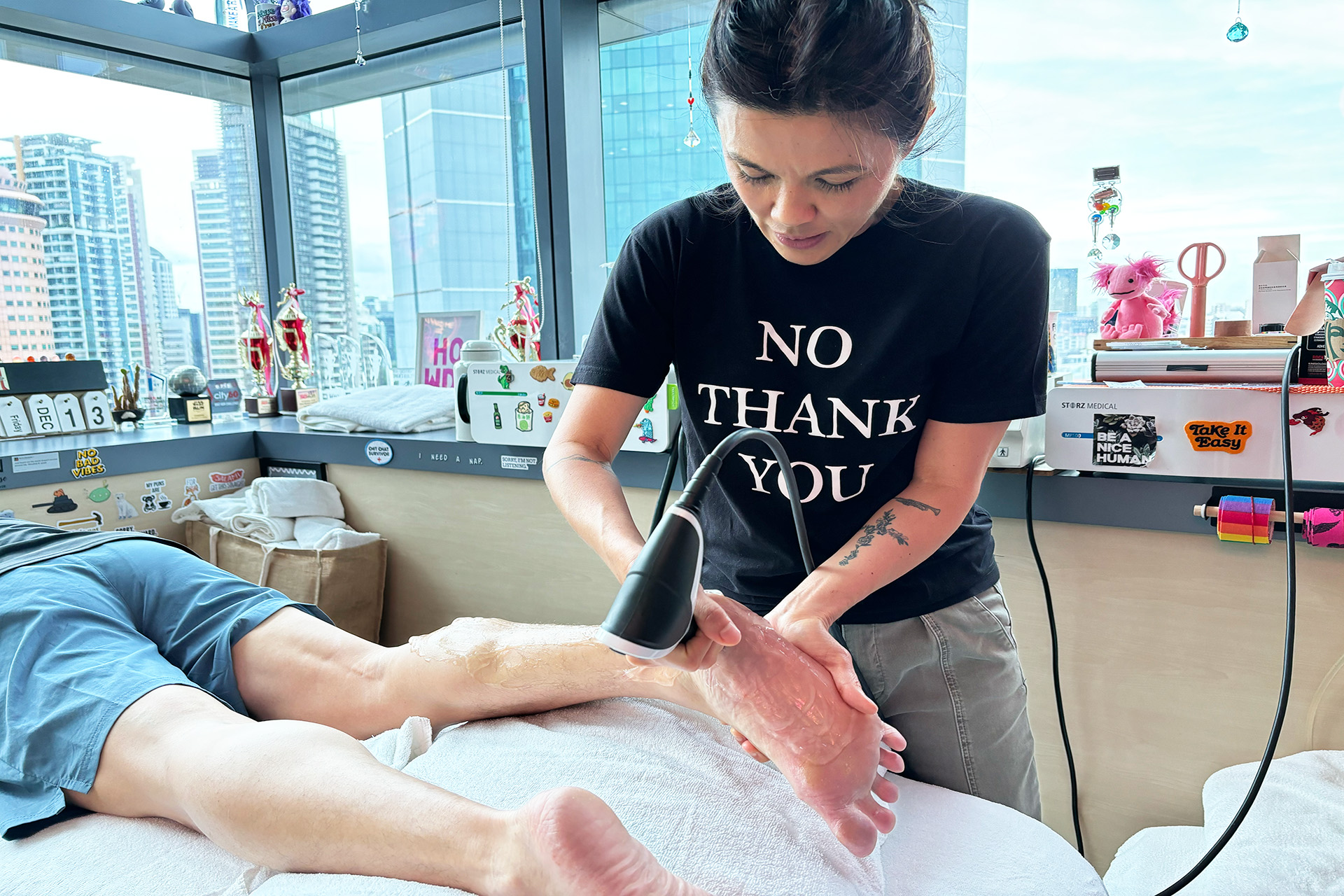
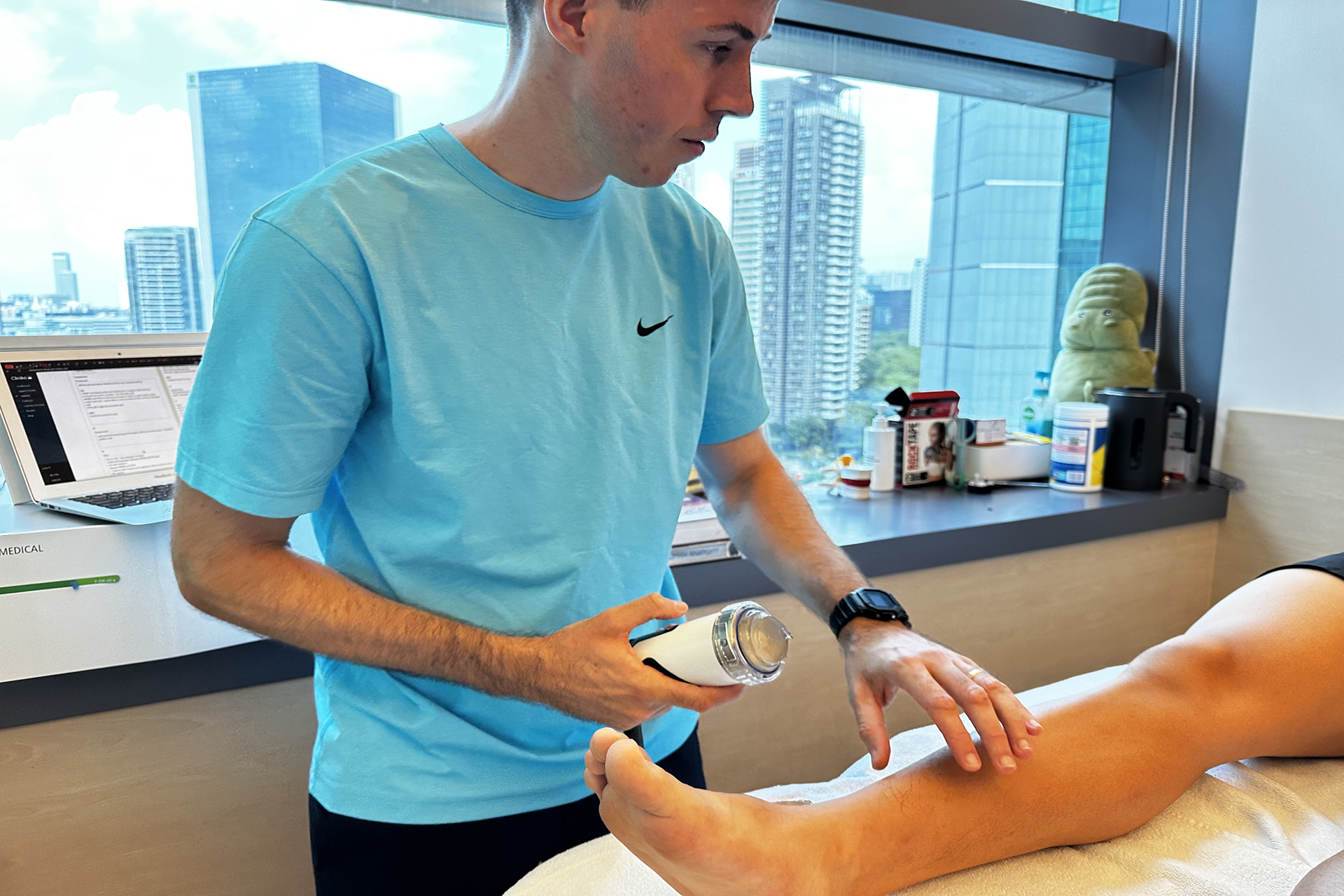
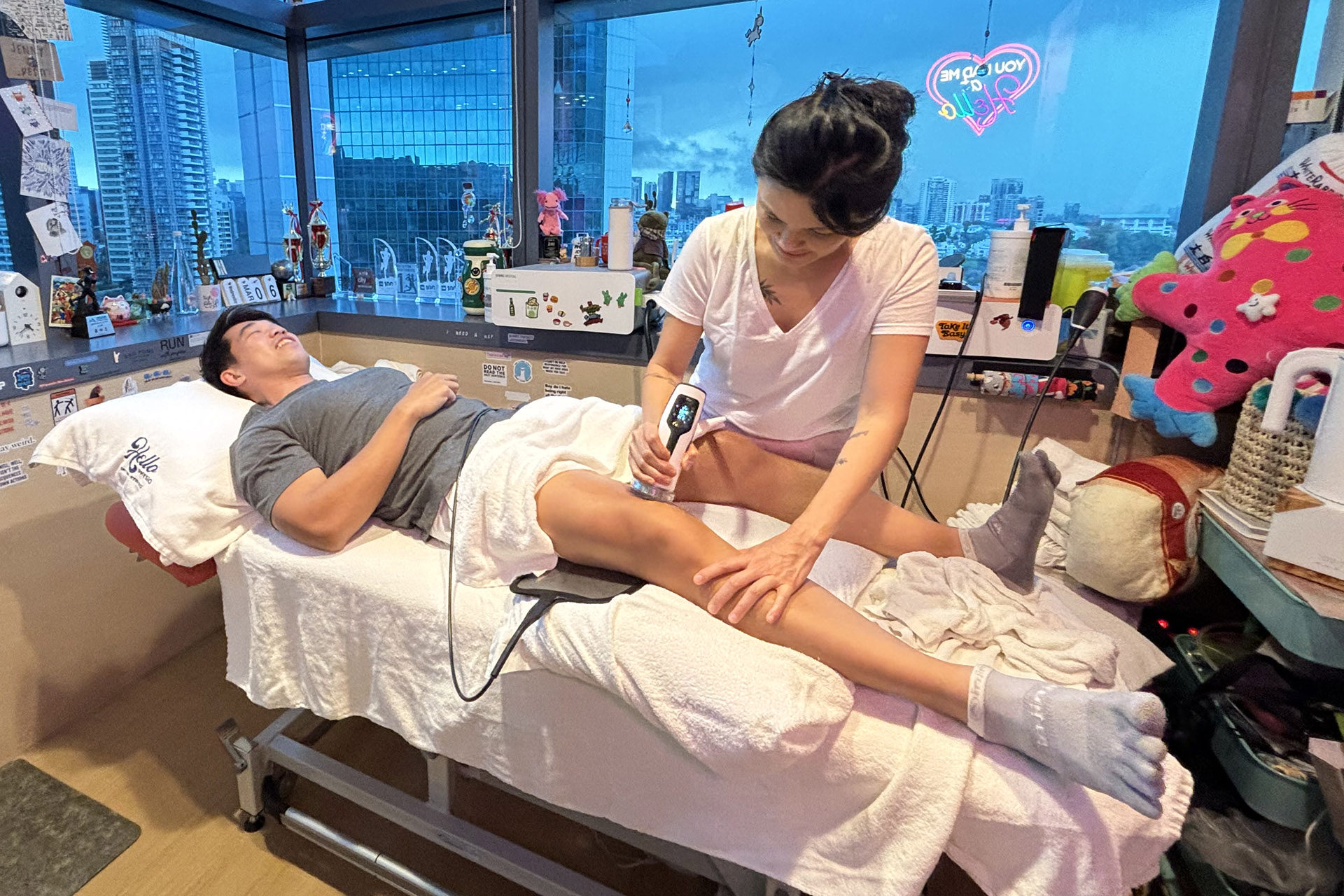
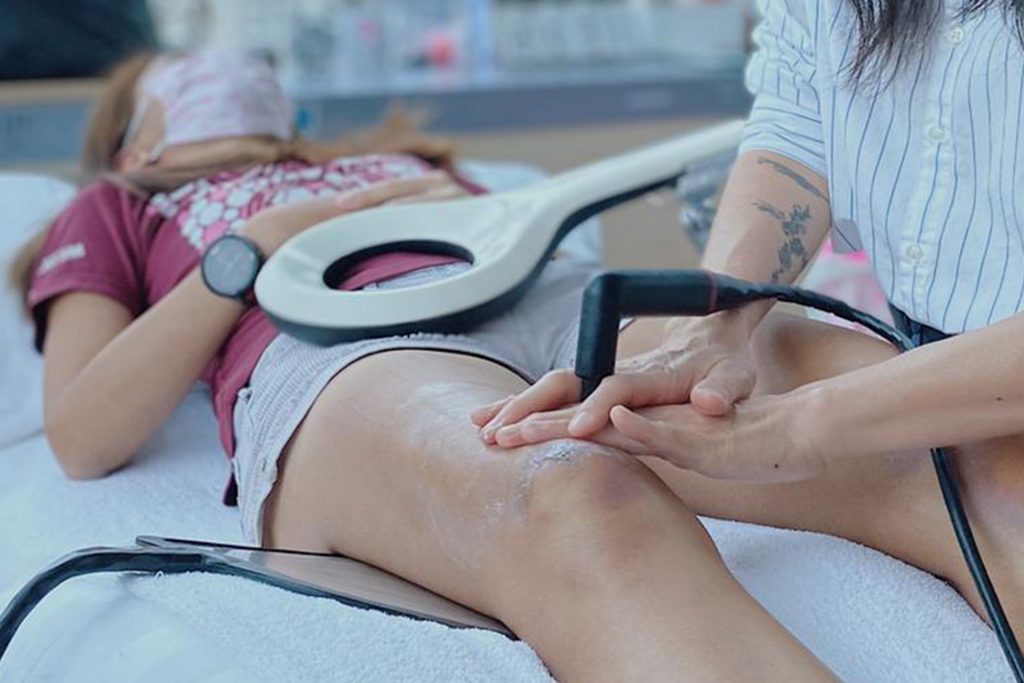
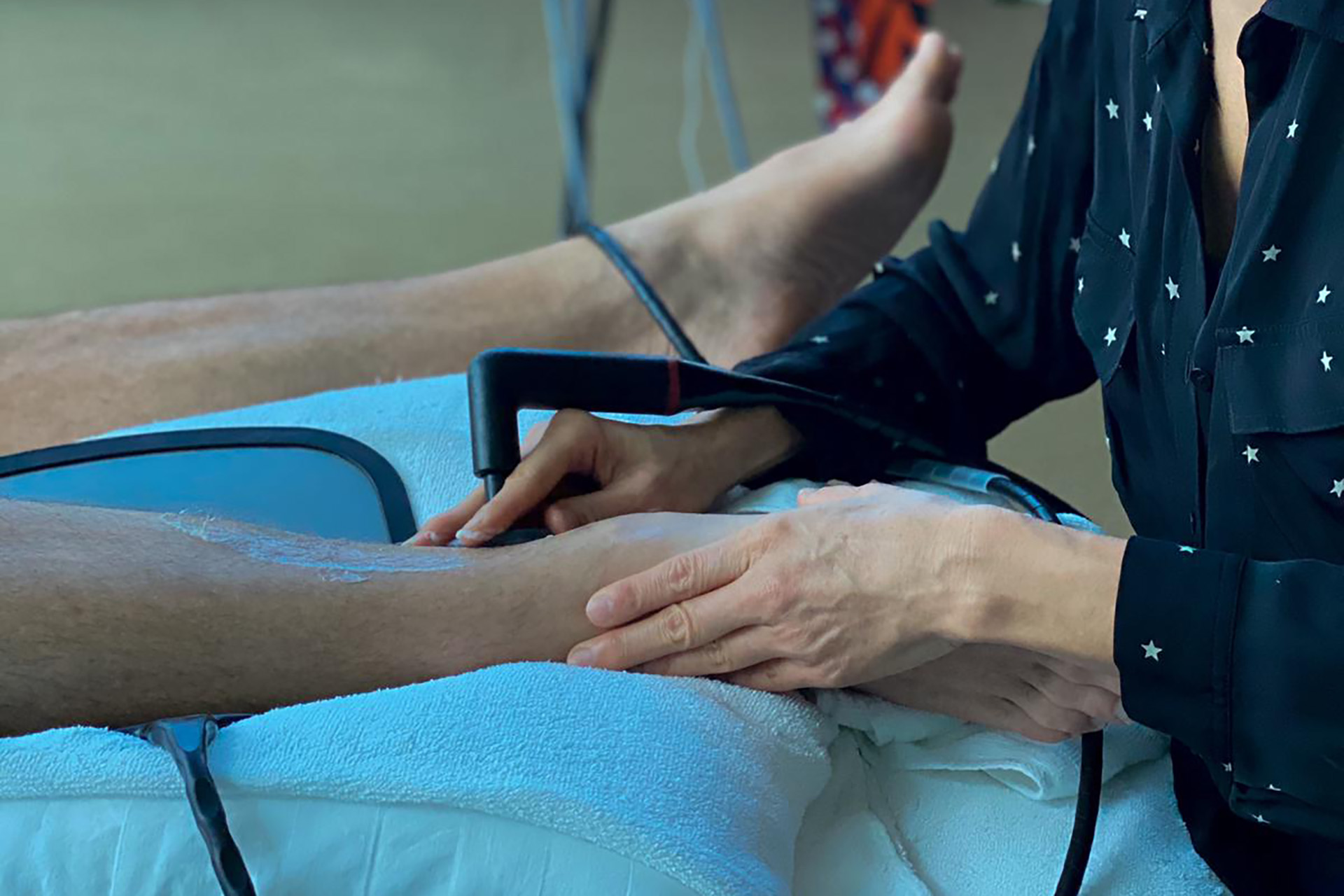
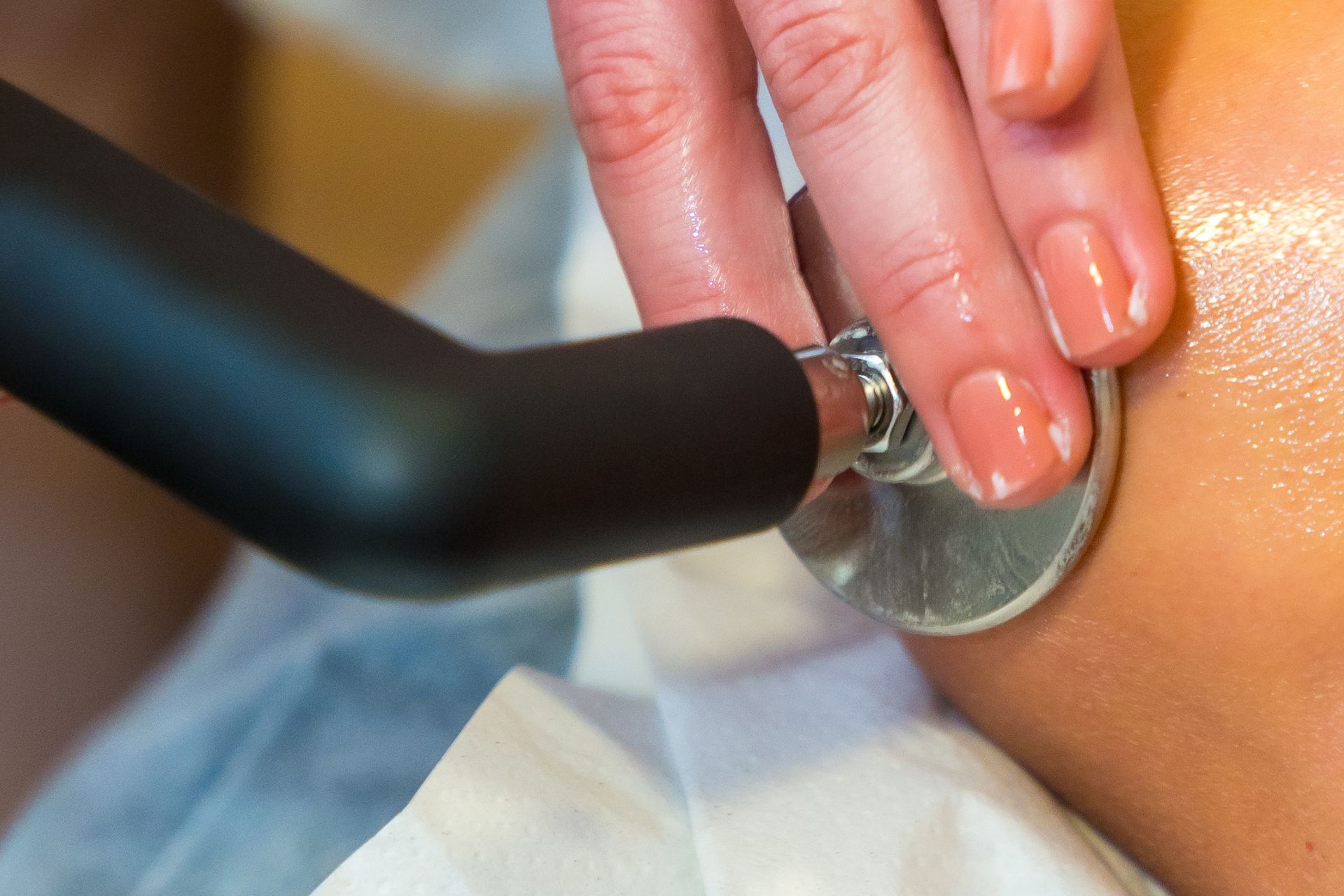
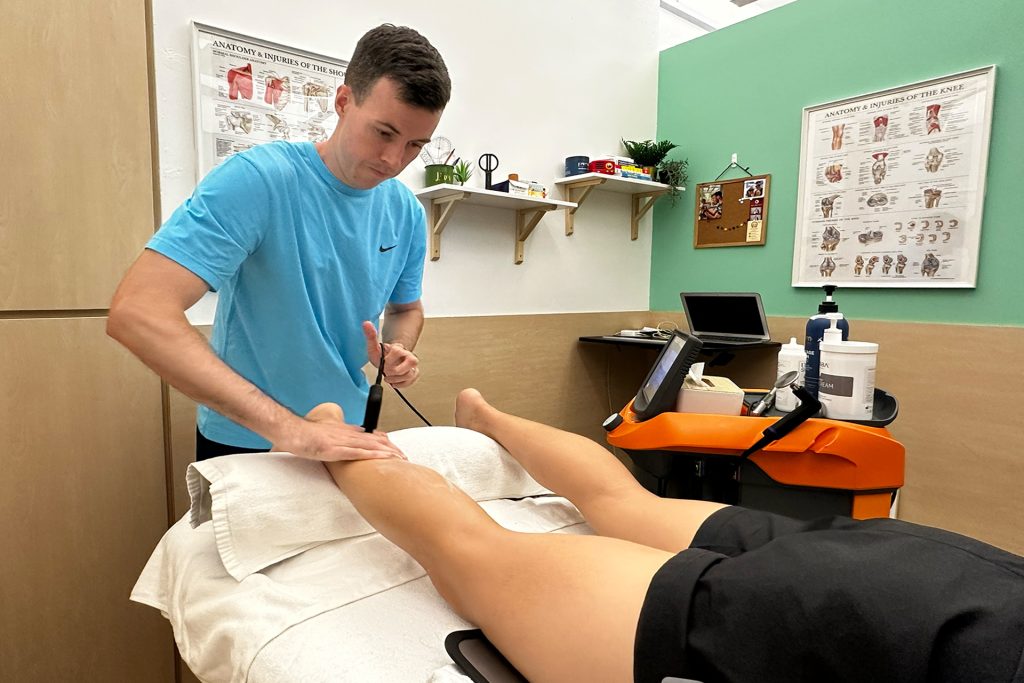
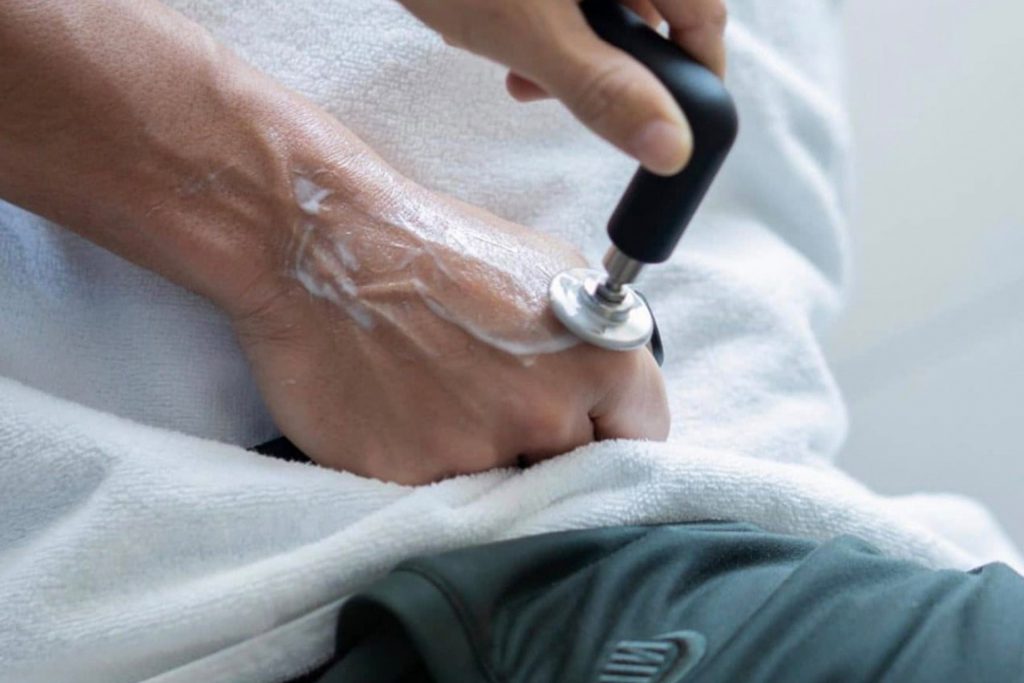
Shockwave Therapy for MCL Sprains
Shockwave Therapy is an innovative treatment that accelerates the healing of ligament injuries by stimulating collagen production and increasing blood circulation. This therapy is beneficial for treating chronic medial collateral ligament sprains, as it breaks down scar tissue and promotes cellular regeneration. The high-energy sound waves encourage faster tissue repair, reducing recovery time and improving knee function.
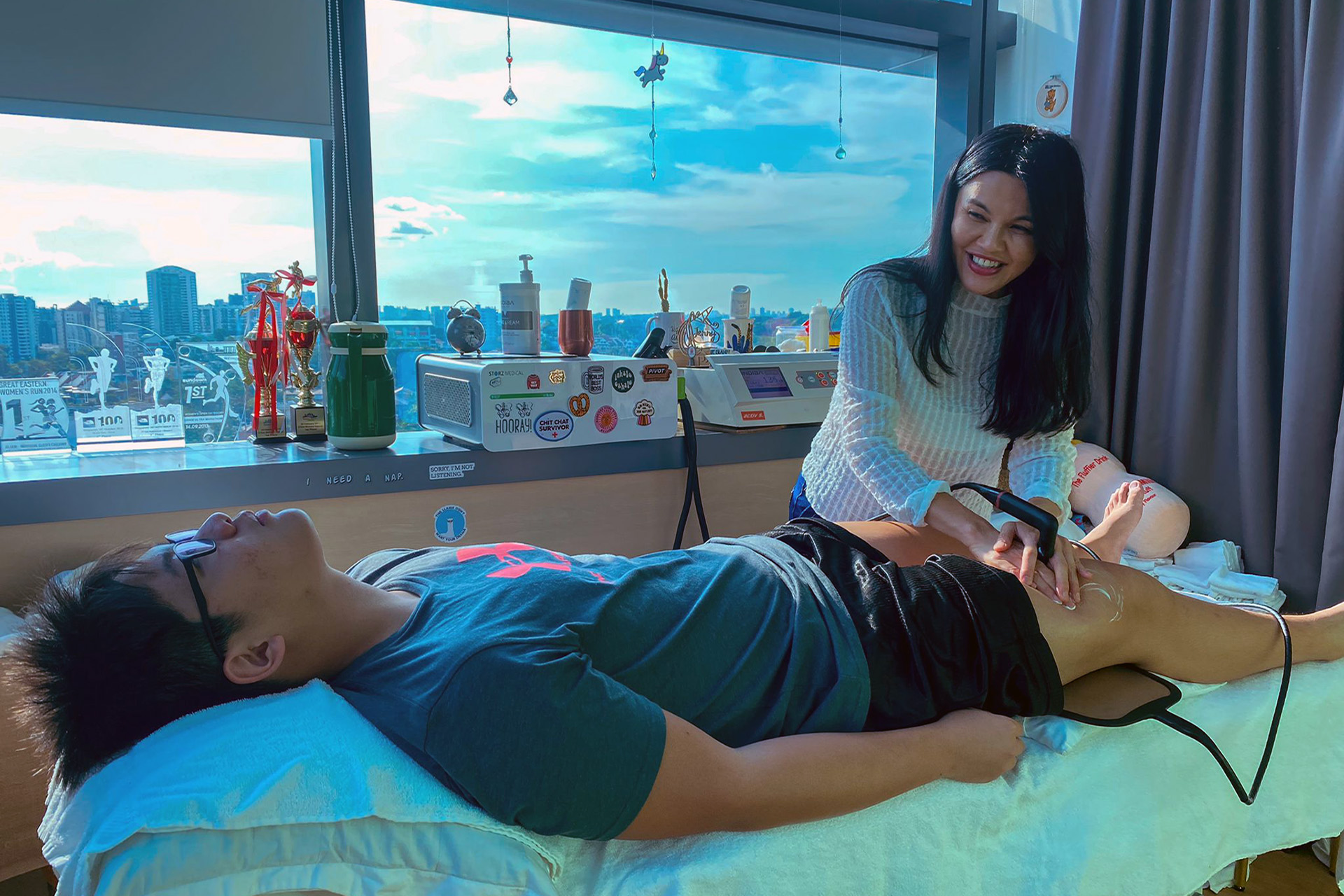
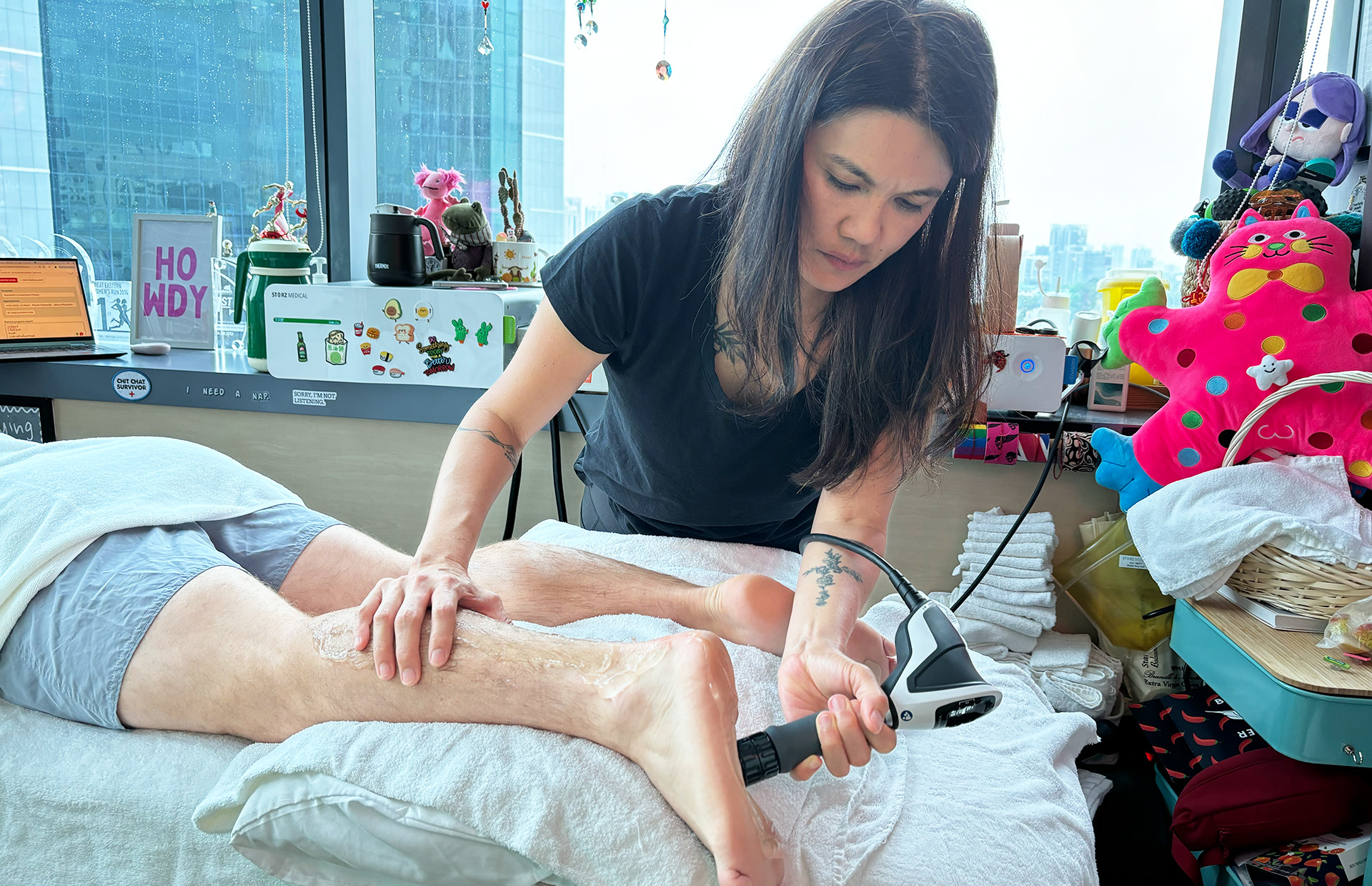
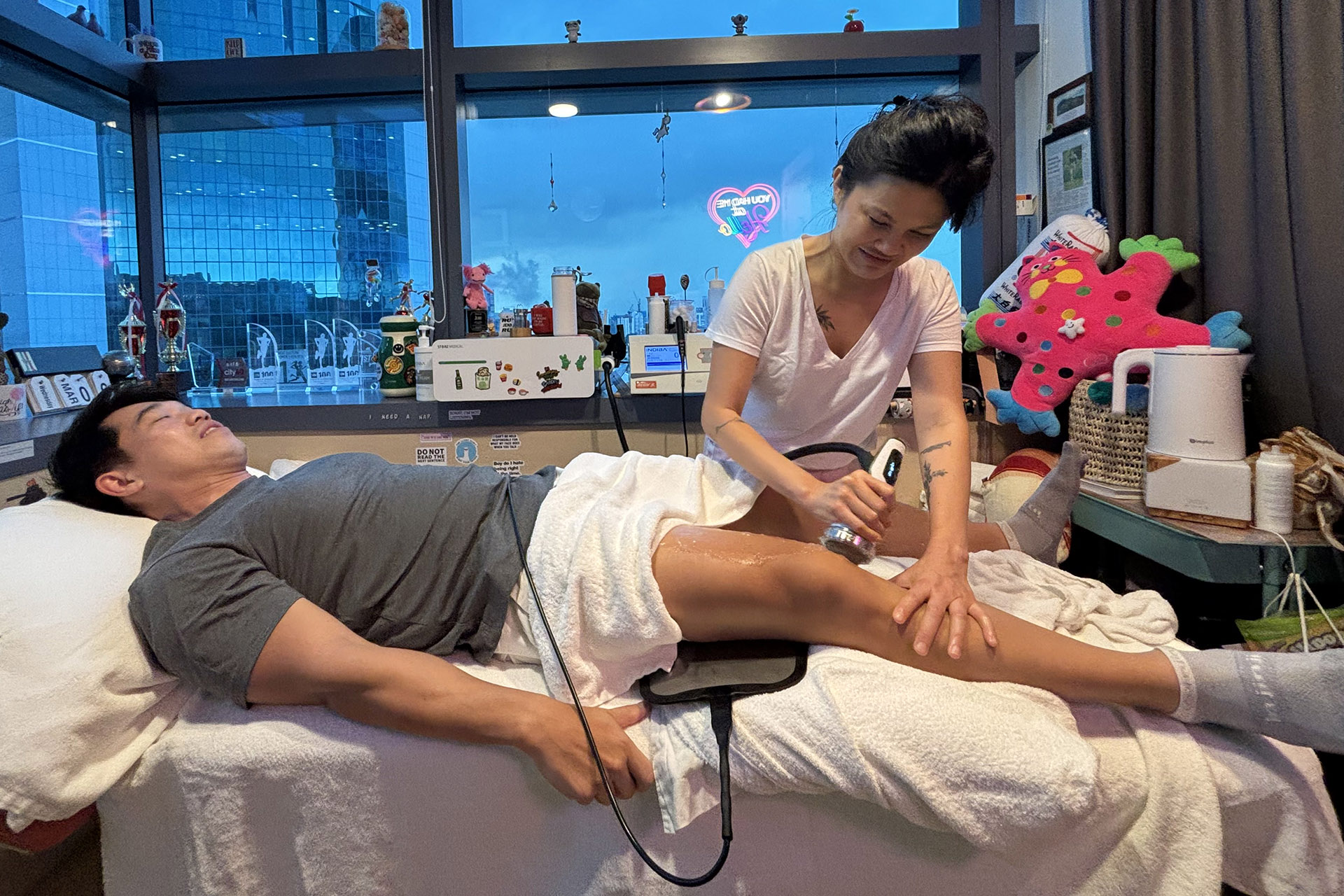
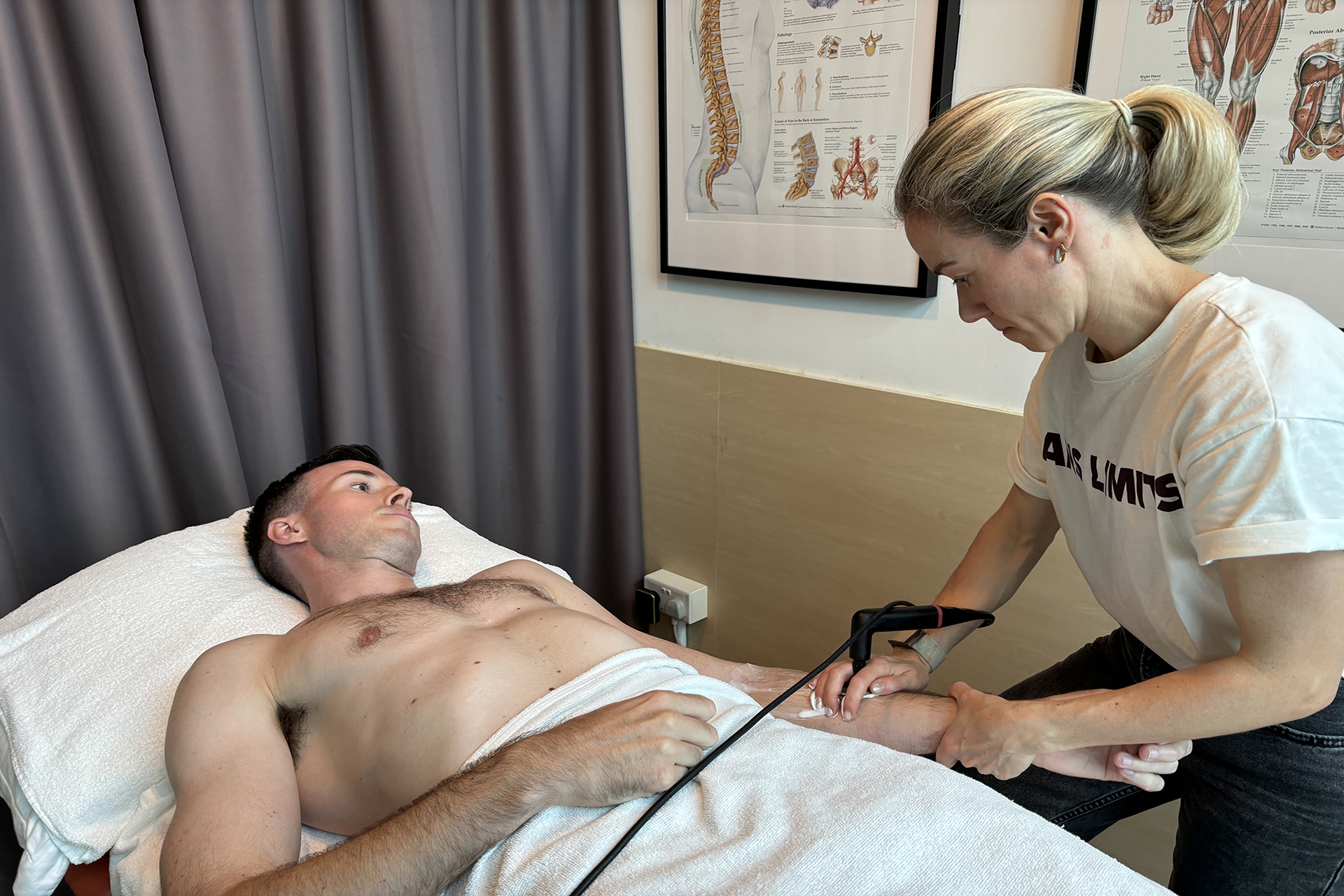
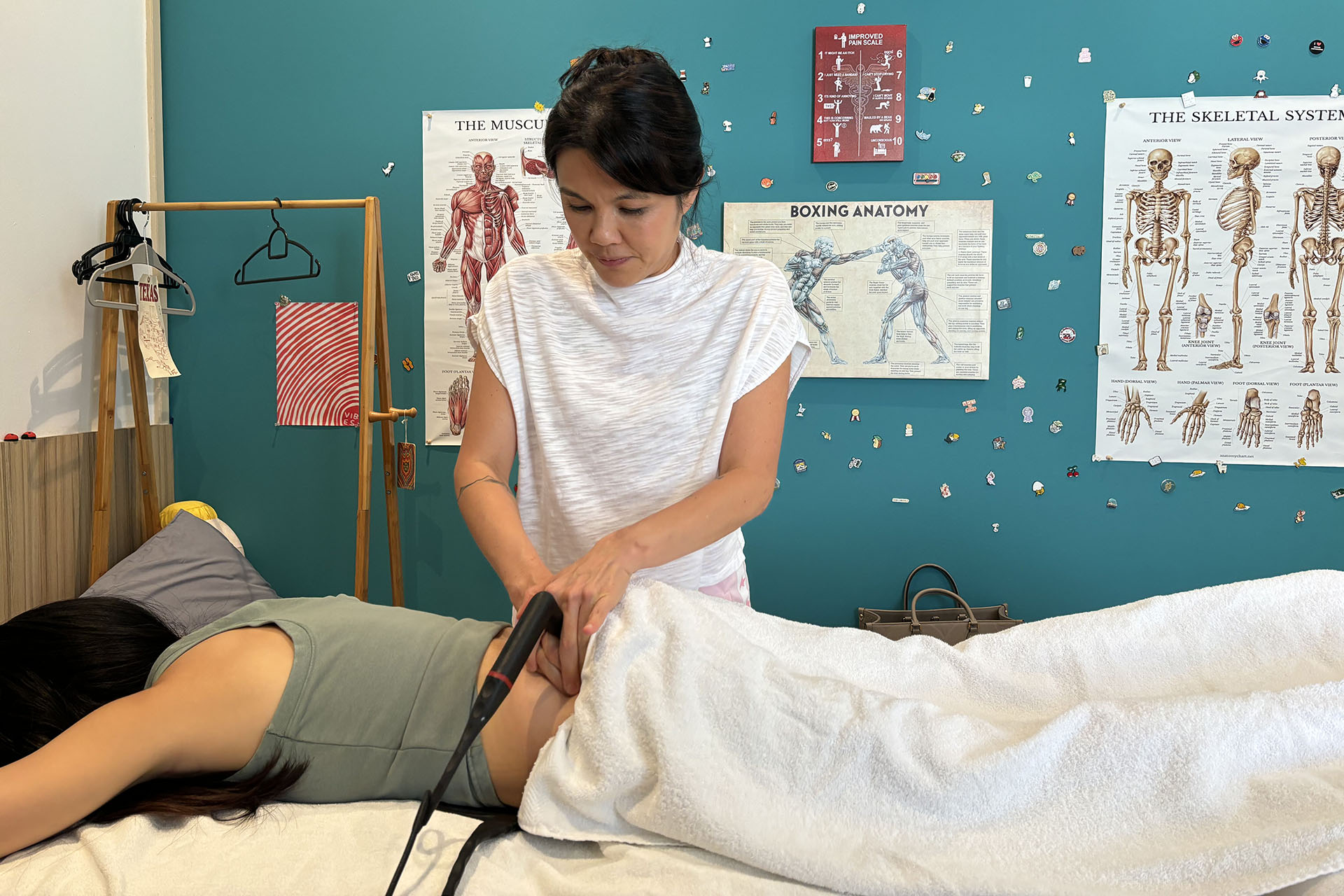
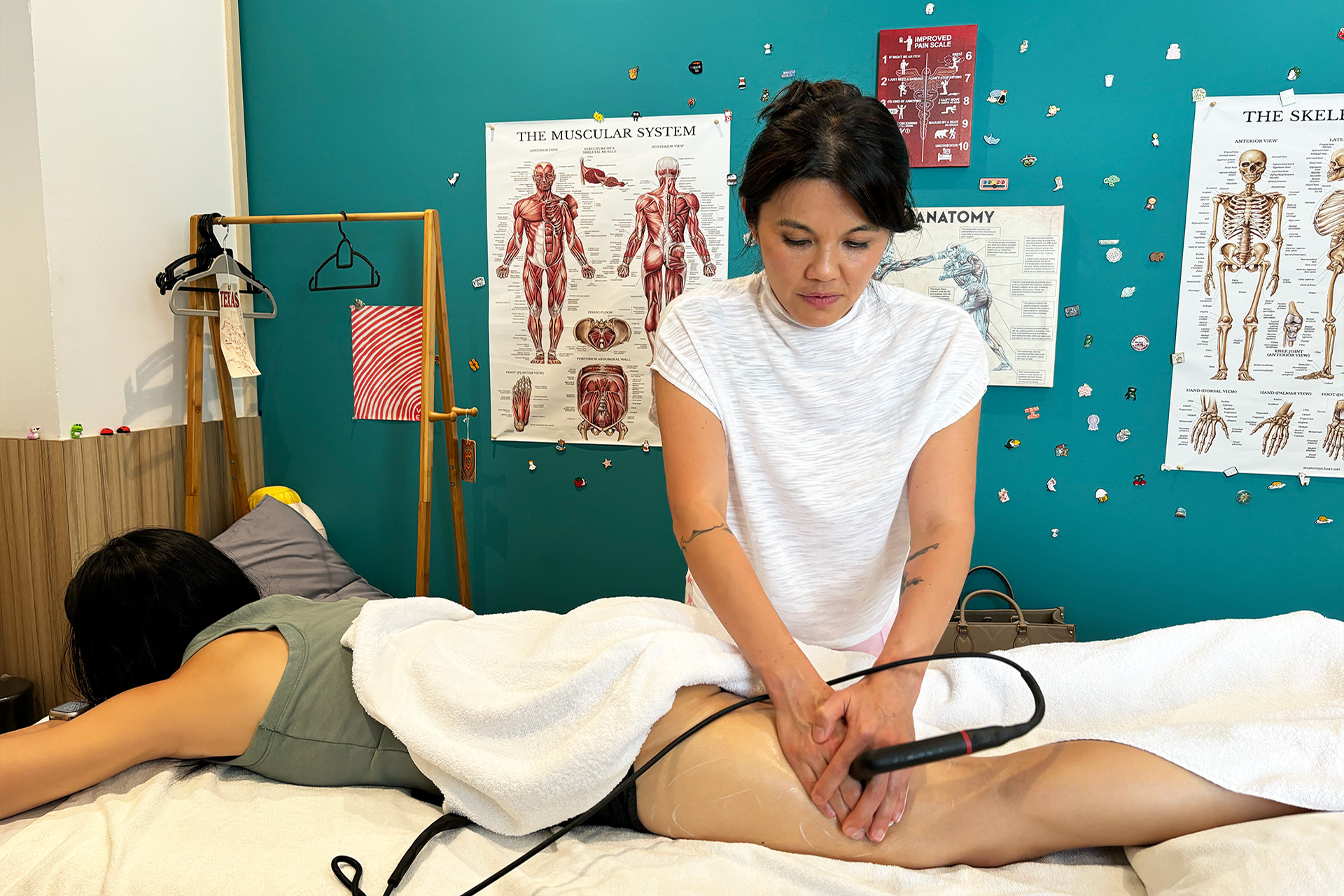
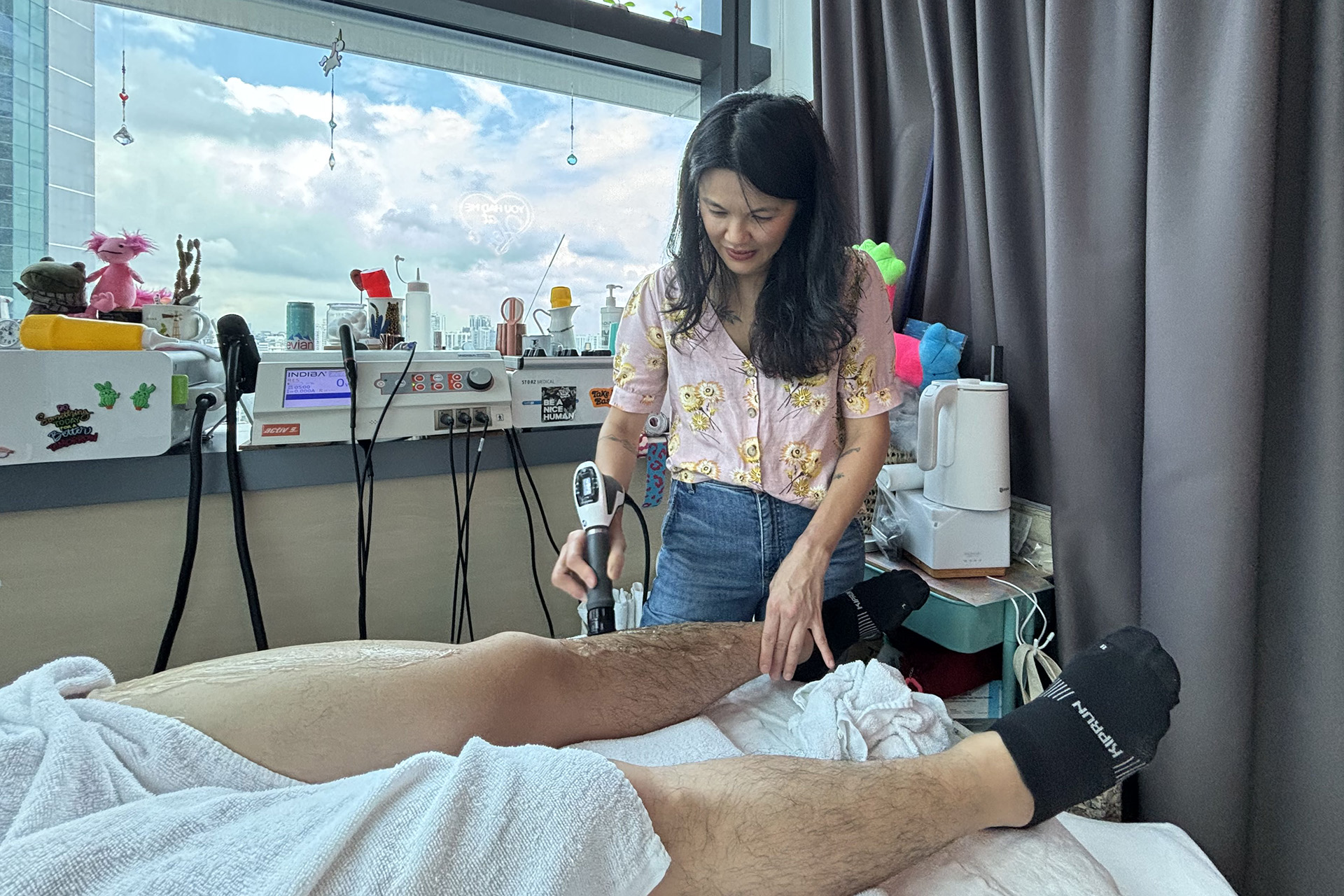
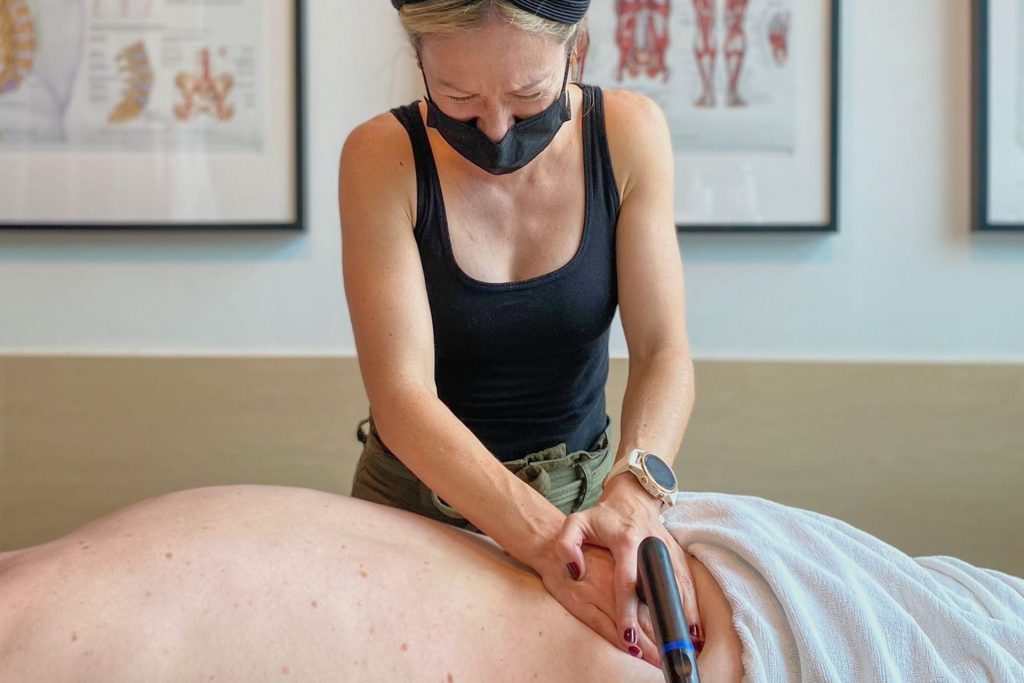
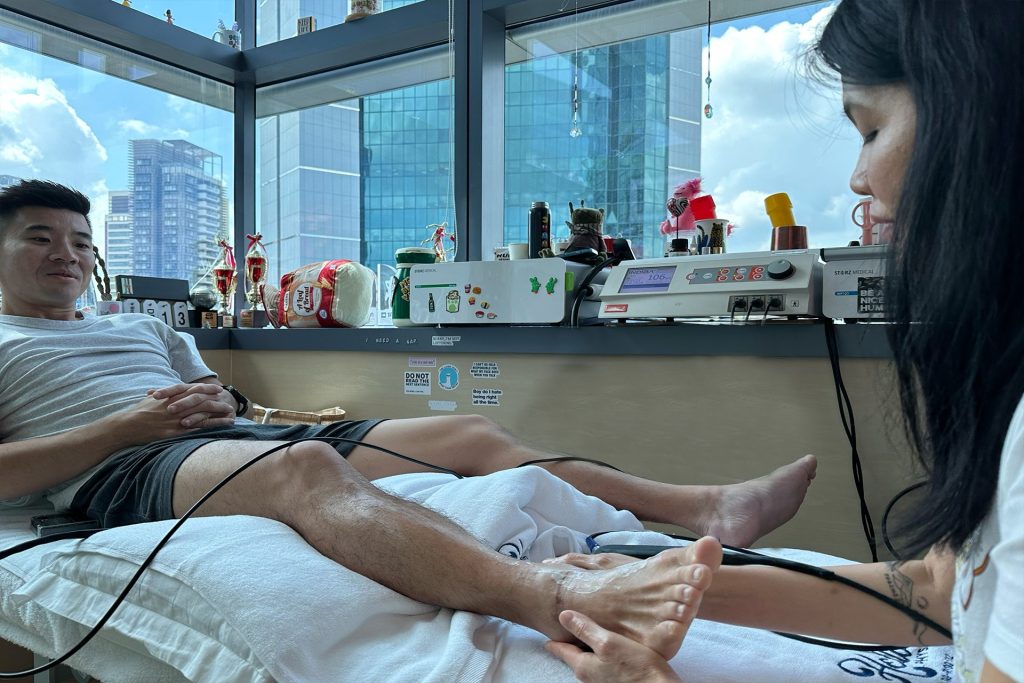
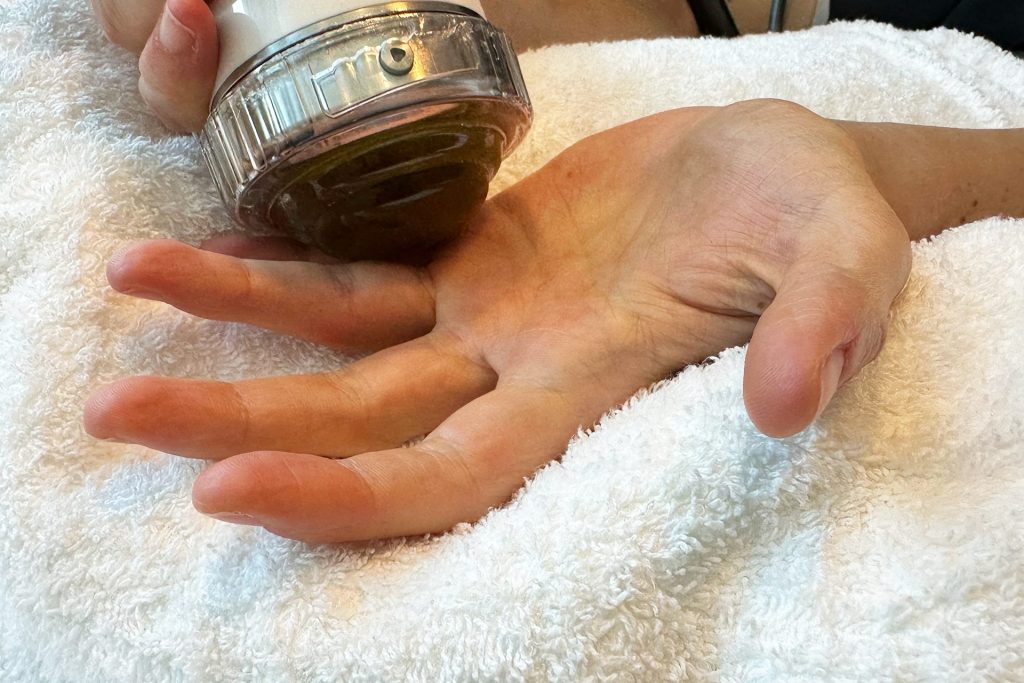
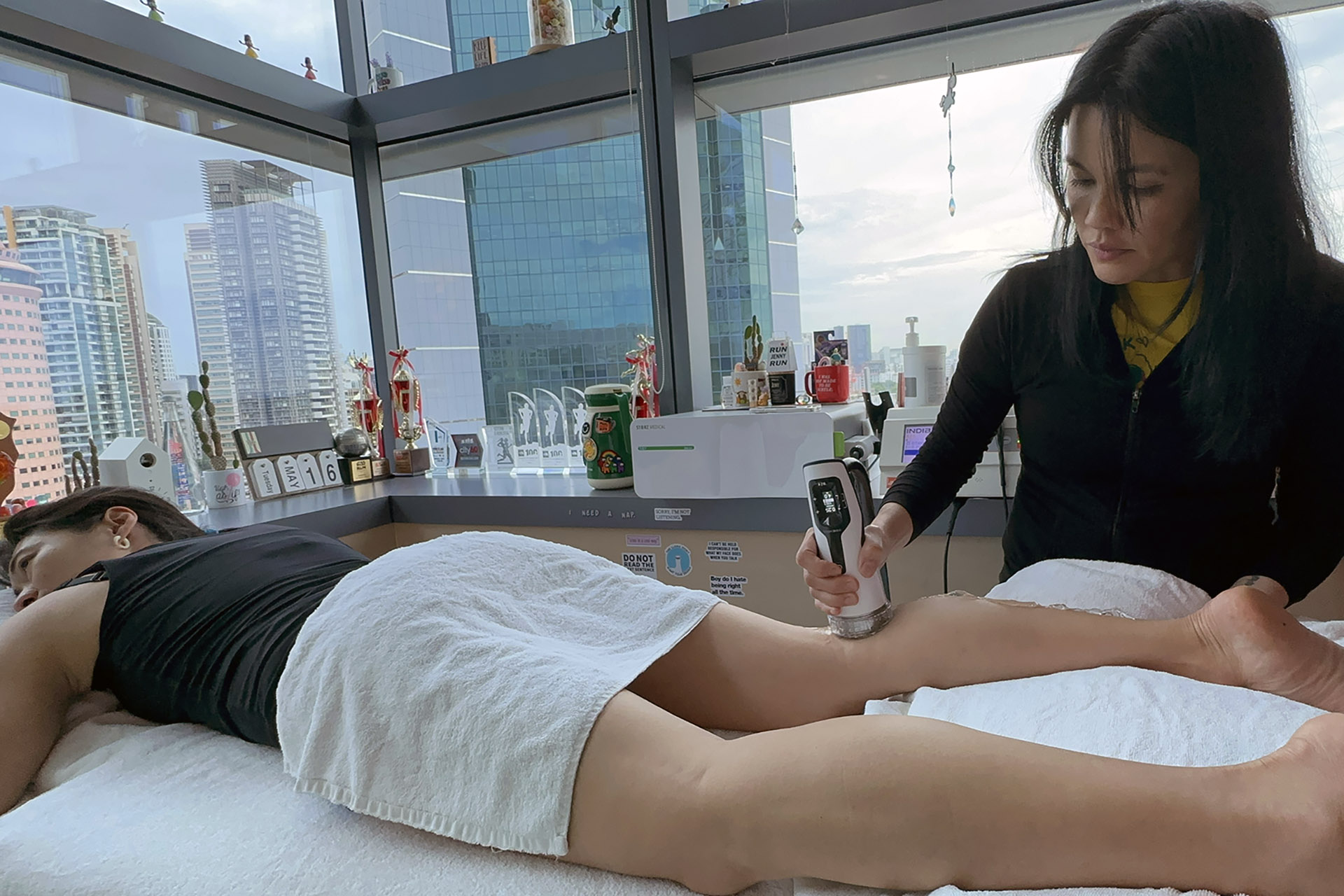
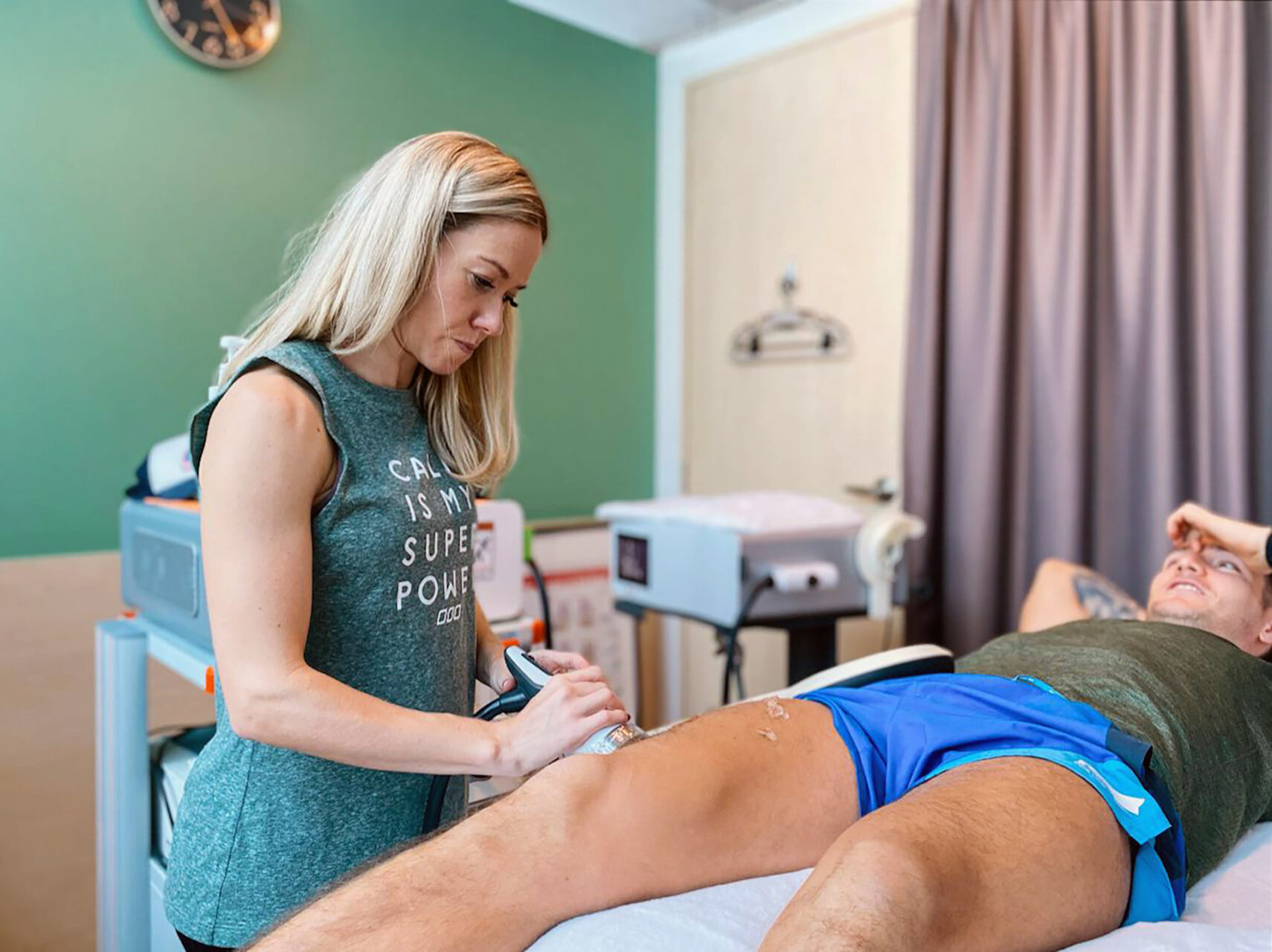
INDIBA® Therapy for MCL Sprains
Another adjunctive therapy for MCL sprain treatment is INDIBA®, which uses radiofrequency energy to stimulate deep tissue healing. By increasing circulation and oxygenation at the cellular level, INDIBA enhances tissue repair, reduces inflammation, and alleviates pain. This modality is especially effective in chronic cases where swelling and stiffness persist, ensuring a smoother rehabilitation process.
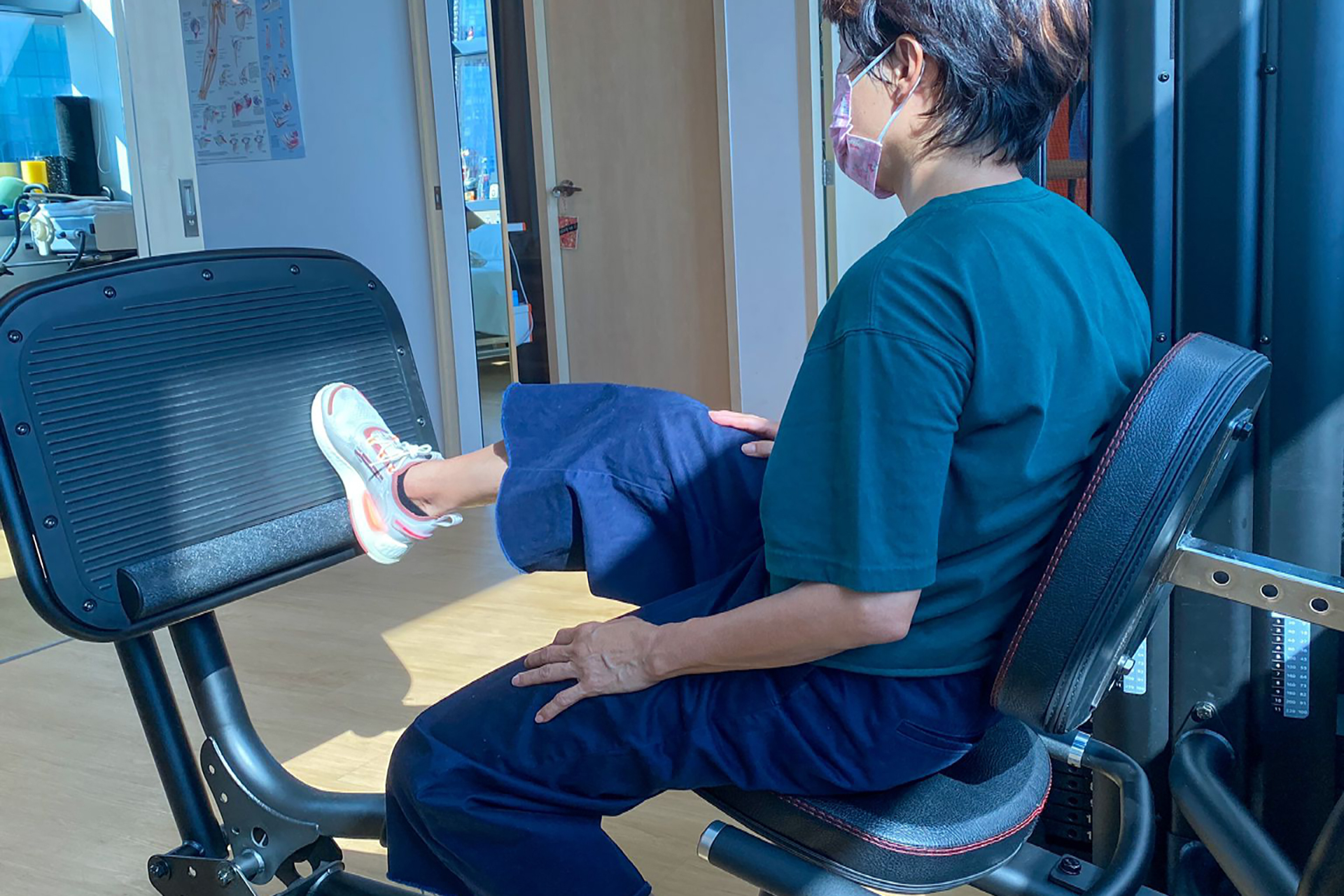
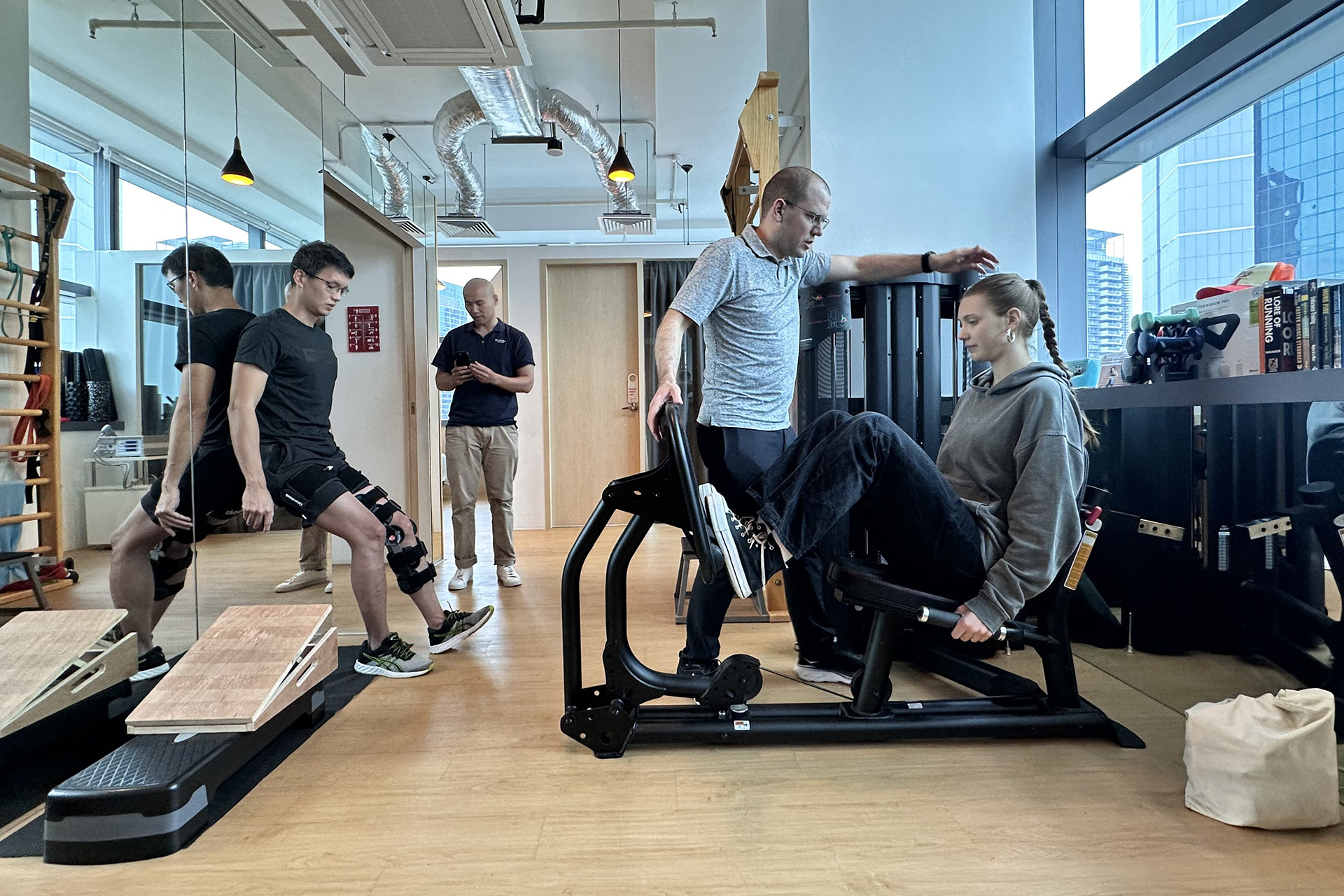
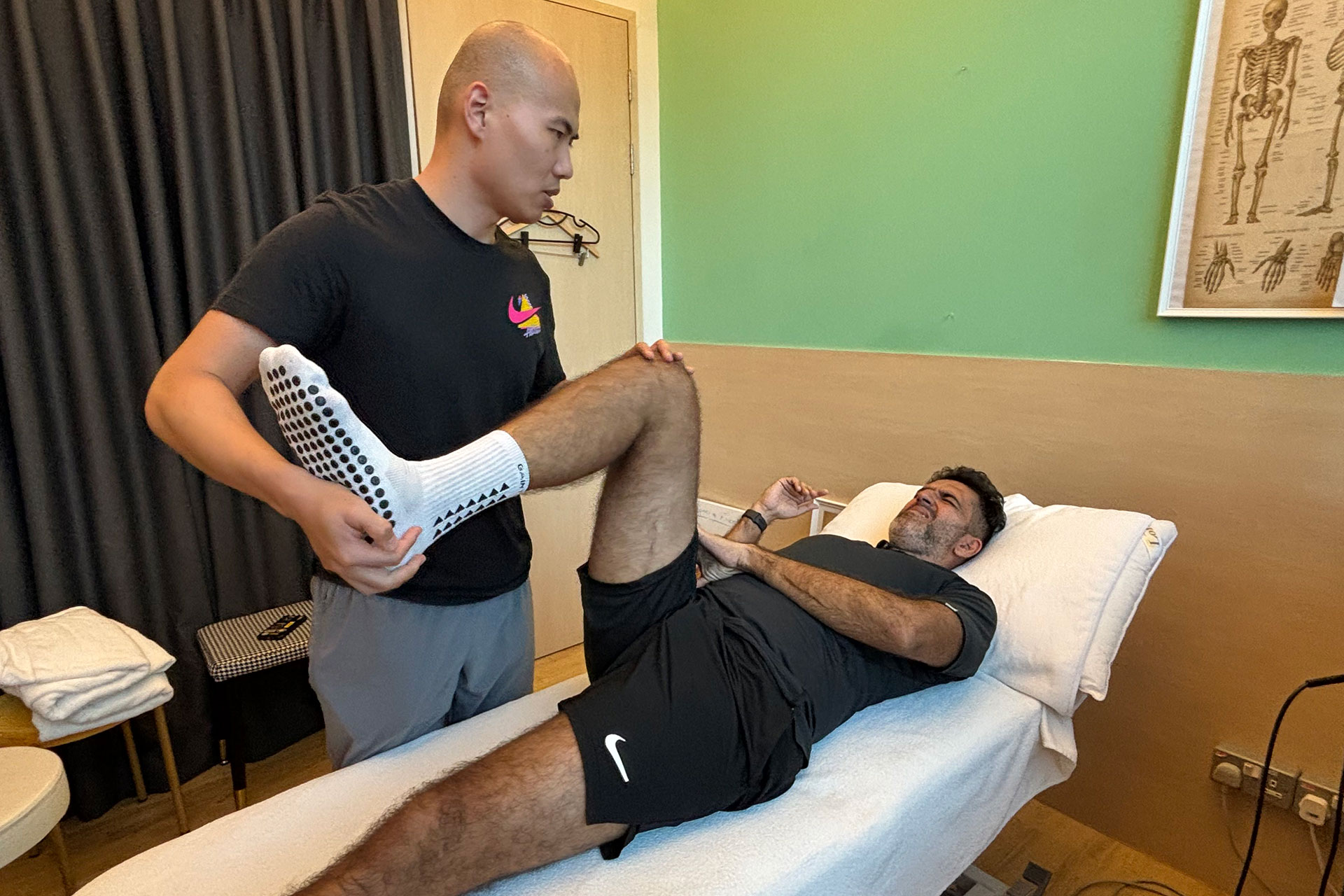
Physical Therapy, Strengthening, and Functional Training
Once pain and inflammation subside, the focus shifts to MCL sprain rehab through targeted strengthening and stability exercises. Strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip stabilizers, helps provide additional support to the MCL and prevents future injuries. Key exercises may include:
- Straight Leg Raises: Strengthens the quadriceps without placing strain on the MCL
- Mini Squats: Improves knee stability while progressively increasing load-bearing capacity
- Glute Bridges: Activates the hamstrings and glutes, enhancing knee support
- Step-Ups: Encourages functional movement and knee control
- Resistance Band Exercises: Improves knee proprioception and lateral stability
These exercises progressively advance based on the individual’s recovery stage, ensuring a smooth transition back to normal activities.
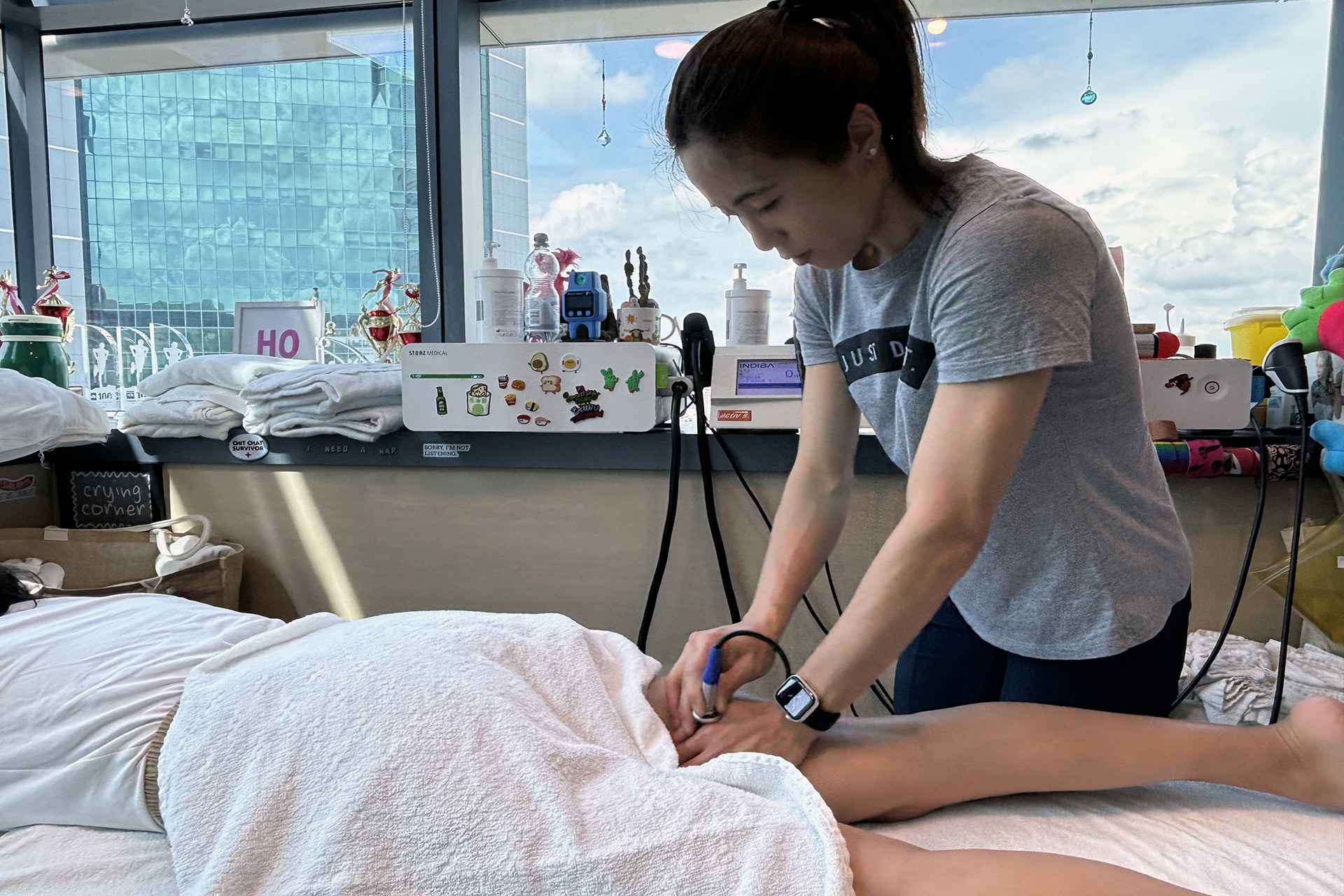
Can I Run with a Sprained MCL?
The answer depends on the severity of the injury. For mild sprains, controlled movement and non-impact exercises like relaxed walking can begin early in rehabilitation. High-impact activities like running should be avoided until sufficient strength and stability are regained. Running too soon can worsen the injury and prolong healing for moderate to severe sprains, or an MCL tear.
A physiotherapist will guide the timeline for safely reintroducing running, ensuring minimal risk of re-injury.
Long-Term Management of Chronic Medial Collateral Ligament Sprains
Without proper rehabilitation, an MCL sprain can become a chronic issue, leading to persistent pain and instability. Chronic medial collateral ligament sprains are often due to incomplete healing, muscle imbalances, or premature return to sports. Long-term management includes ongoing strength training to prevent re-injury. Biomechanical assessments may identify movement patterns that increase injury risk. Neuromuscular training enhances balance and proprioception for better knee control. In some cases of chronic MCL sprains, surgery might be recommended, depending on the severity of the injury and other factors.
For individuals dealing with persistent MCL pain, a combination of physiotherapy, Shockwave Therapy, and INDIBA® can help resolve chronic symptoms and restore full function.

Preventing MCL Injuries
Preventing MCL injuries requires proper training, equipment, and technique. Proper protective gear, such as knee pads and shin guards, can help protect the knee from direct blows and impacts. Warming up and stretching before engaging in physical activity prepares the muscles and ligaments for the demands of the sport, reducing the risk of injury.
Strengthening the thigh muscles through exercises like squats and lunges can provide additional support to the knee joint, enhancing stability. Improving knee alignment and biomechanics through proper training and technique can prevent undue stress on the MCL. Avoid overtraining and take regular breaks to rest and recover. Maintaining a healthy weight also reduces stress on the knee joint, further protecting it from injury.
Relationship with Other Knee Injuries
MCL injuries often occur with other knee injuries, such as anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears, posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) tears, meniscal tears, cartilage damage, and bone fractures. These combined injuries can complicate the diagnosis and treatment process, requiring a comprehensive approach to address all affected areas.
Treating MCL sprains alongside other knee injuries necessitates a thorough assessment by a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that addresses all related injuries. Surgery may sometimes be necessary to repair or reconstruct multiple knee injuries, ensuring proper healing and preventing further complications.
Regain Strength and Stability with Expert MCL Sprain Treatment
Recovering from an MCL sprain requires a well-structured physiotherapy program that incorporates pain management, strengthening, and adjunctive therapies like Shockwave Therapy and INDIBA. Professional guidance ensures optimal healing and a safe return to activities, whether dealing with an acute injury or a chronic medial collateral ligament sprain.
If you’re seeking expert therapy for an MCL sprain, HelloPhysio provides personalized treatment plans tailored to your recovery needs. Contact us today to start your rehabilitation journey to regain knee strength and stability.